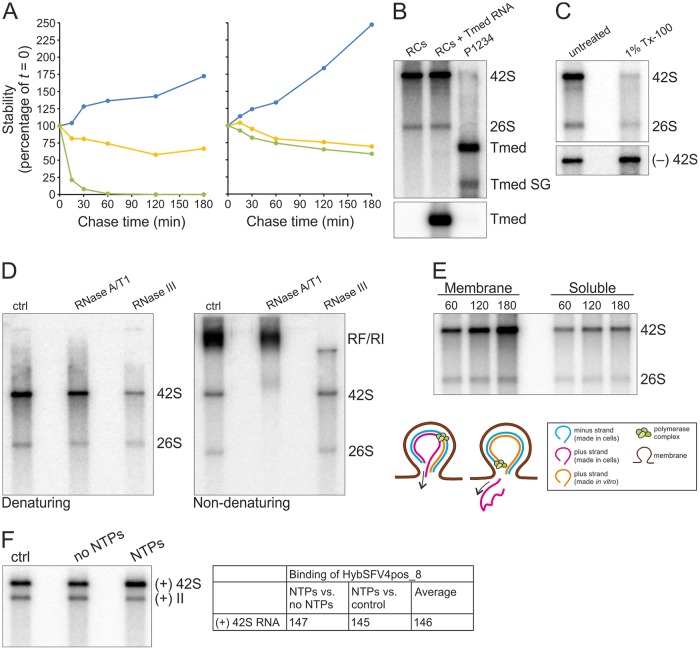
FIG 9.
Characterization of the in vitro replication activity of the purified RCs. (A) Stability of newly synthesized SFV genomic RNA. After a 60-min replication assay, [32P]CTP incorporation was blocked by the addition of 100 μM 3′-dCTP, and incubation at 30°C was continued for an additional 180 min. The graph on the left represents an assay with 10-fold-diluted S7 and on the right with the purified RCs. At the indicated chase times radioactivity in 42S was quantified (yellow). As a control, a reaction without 3′-dCTP was quantified (blue). In addition, in vitro transcript of Tmed added in the reaction at a 0-min chase was quantified by in-gel hybridization (green). All values are presented as percentages of the values at the 0-min chase. (B) Purified RCs and additional exogenous template. Replication assay reaction mixtures were incubated for 2 h. RCs indicates [32P]CTP incorporation by the purified RCs. RCs + Tmed RNA shows incorporation by the purified RCs after an exogenous Tmed RNA transcript was added. As a control, [32P]CTP incorporation by the P15 membrane fraction from cells transfected with the P1234 polyprotein and Tmed template plasmids is shown, and genomic and subgenomic (SG) Tmed are indicated. The lower panel shows the presence of Tmed, detected by in-gel hybridization. (C) Detergent stability and sensitivity. Purified RCs were treated with 1% Tx-100, followed by an assay to detect replication (upper) and in-gel hybridization to detect the minus-strand template RNA (lower). (D) ssRNA and RF/RI forms of in vitro-synthesized RNAs. After a 2-h replication assay with the purified RCs, RNA was isolated and treated with RNase A/T1 or III under high-salt conditions to specifically digest ssRNA or dsRNA, respectively, and analyzed under denaturing (left) or nondenaturing (right) conditions. (E) Release of newly made RNA. A replication assay was performed with the concentrated purified RCs, and after 60-, 120-, and 180-min replication reactions, aliquots were removed to prepare pellet and supernatant fractions, followed by RNA isolation and analysis in a denaturing agarose gel. The schematic shows how [32P]CTP is incorporated into viral RNA during in vitro RNA synthesis, resulting in dsRNA containing a plus strand synthesized both in cells (indicated by magenta) and in vitro (indicated by orange). After a round of replication and release of the previous plus strand, an RC contains only the in vitro-synthesized plus strand if replication is semiconservative. (F) Increase in the amount of RNA during in vitro replication. After a 4-h replication assay with the purified RCs and unlabeled NTPs, RNA was isolated and genomic RNA was detected by in-gel hybridization. No NTPs indicates a reaction without added NTPs, and ctrl indicates a sample without any incubations before RNA isolation. 42S RNA was quantified, and average percentages from two independent experiments are shown in the table.