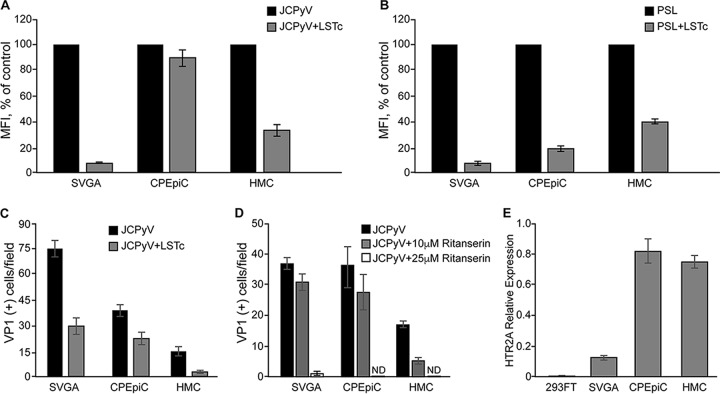
FIG 3.
LSTc competes with PSL and virus for binding to cells and inhibits infection. (A) Purified, labeled JCPyV was incubated with soluble receptor LSTc, and then binding to cells was assayed by flow cytometry. LSTc inhibited JCPyV binding to SVG-A and HMC but did not inhibit binding to CPEpiC. (B) The LSTc binding lectin, PSL, was incubated with LSTc, and then PSL binding to cells was assayed by flow cytometry. LSTc inhibited binding of PSL to all three cell types. (C) Purified JCPyV was incubated with LSTc and then used to directly infect cells. LSTc inhibited infection of all three cell types. (D) The 5-HT2R antagonist inhibits infection of SVG-A and HMC by JCPyV. Cells were treated with 25 μM and 10 μM ritanserin and then challenged with JCPyV. The 25 μM dose of ritanserin abolished infection of SVG-A but was toxic to the primary CPEpiC and HMC. The lower dose, 10 μM, was not sufficient to inhibit infection of SVG-A or CPEpiC but did inhibit infection of HMC. (E) HTR2A mRNA levels measured by quantitative PCR (qPCR) are represented. Error bars represent standard errors of the mean for three independent experiments performed in triplicate.