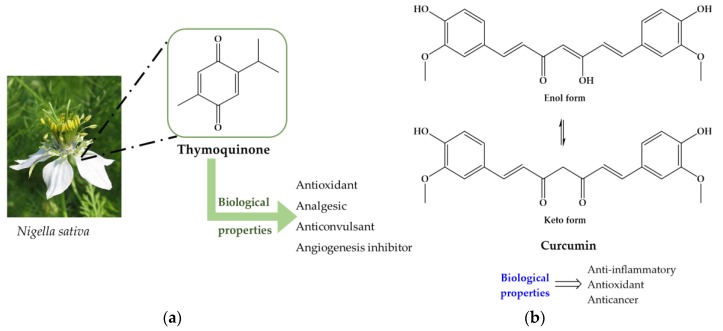
Figure 7.
(a) Nigella sativa and its therapeutically active constituent, thymoquinone, responsible for diverse biological properties; (b) Chemical structures of curcumin and its biological properties. Curcumin is the principal curcuminoid of Curcuma longa. It is a diarylheptanoid, which is a natural phenol that exists in enolic form in organic solvents and as a keto form in water.