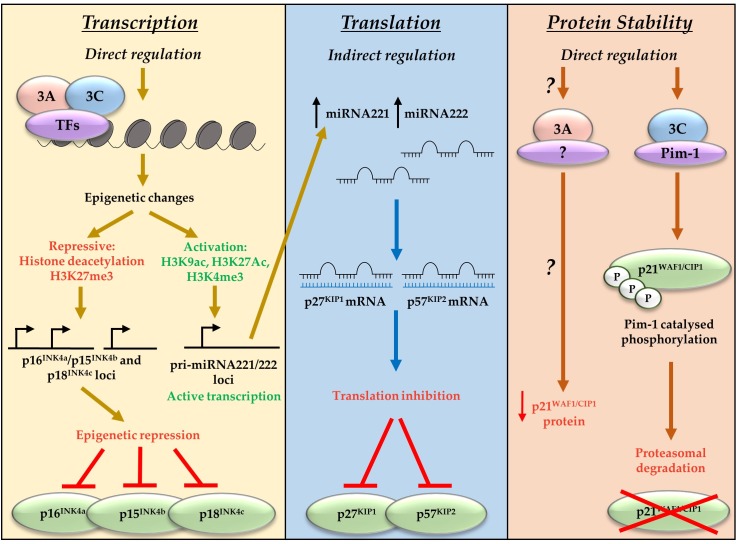
Figure 2.
EBNA3A and EBNA3C regulate CDKI at a transcriptional, translational, and protein levels. EBNA3A and EBNA3C bind cell transcription factors (TFs) including RBP-Jκ, CBF, and IRF4. This results in polycomb complex recruitment and deposition of chromatin marks on the loci of target genes. These chromatin marks can either repress transcription (the CDKIs p16INK4a, p15INK4b, and p18INK4c) or activate transcription (miRNA221/222). EBNA3-mediated activation of miRNA221/222 leads to subsequent repression of the CDKI p27KIP1 and p57KIP2 via translation inhibition. EBNA3A and EBNA3C can also repress CKDI by targeting them for degradation. EBNA3A mechanisms are unclear, but EBNA3C has been shown to mediate Pim-1 catalysed phosphorylation and subsequent proteasomal degradation of p21WAF1/CIP1.