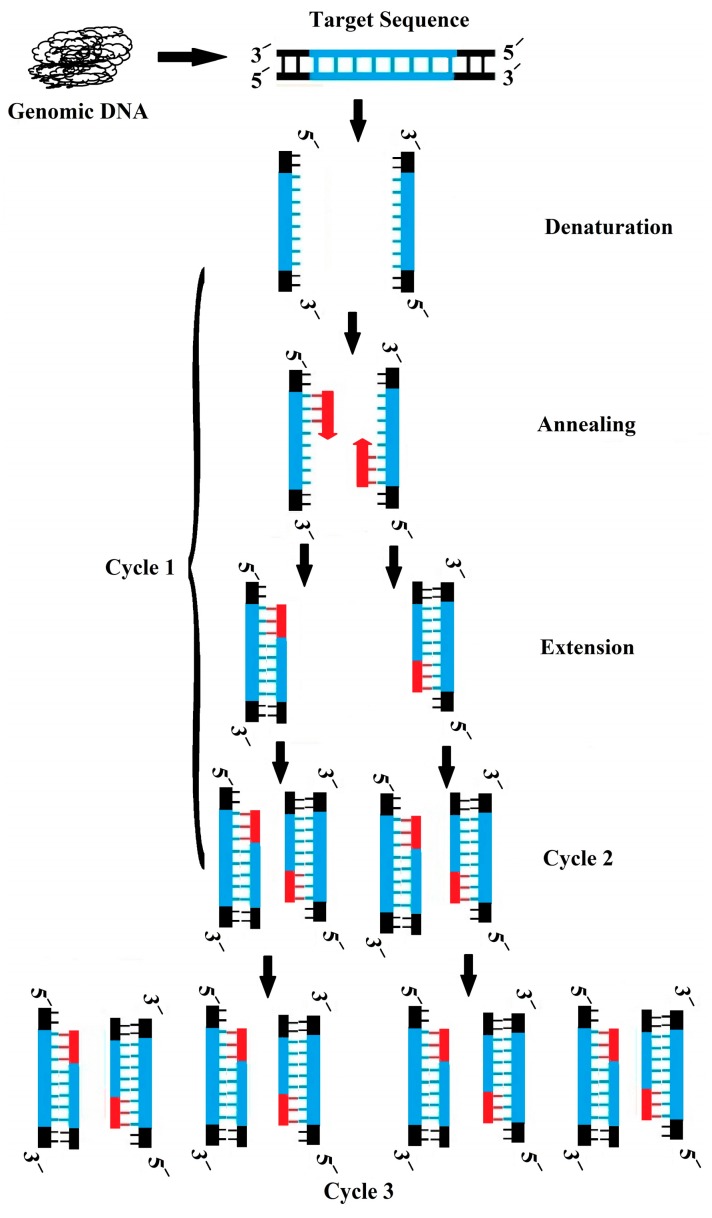
Figure 12.
The principle of polymerase chain reaction (PCR); through denaturation period, increase in the temperature of the media (more than 90 °C) lead to separation of the DNA duplex in the form of single strands. Reduction of temperature to around 50 °C (depending to the primer) in the annealing step provides the condition for the single strand nucleic acids, including the primers, to re-hybrid in the form of double strand DNA. Thereafter, though extension step, an amplifier enzyme is able to use the 3′ end of the primer to extend the primer based on the complementary template DNA. These steps are usually repeated more than 30 times (depending on the concentration of the template DNA) to increase the numbers of the fragment sufficient for visibility on a gel. Since the primers are specifically designed for a special fragment of the genome, the amplification is specifically performed on that area of the genome.