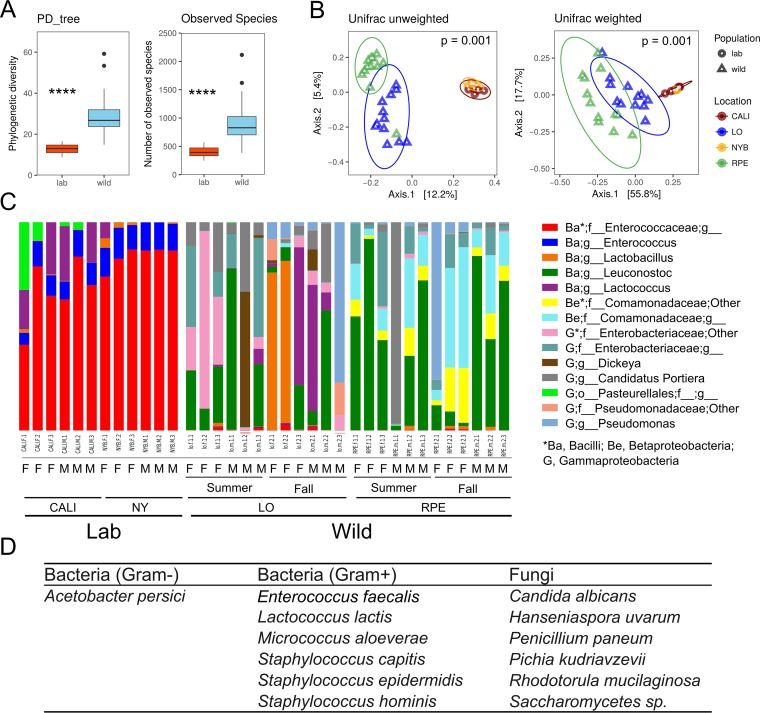
FIG 2 .
The diversity of microbes in wild D. suzukii flies is much higher than in laboratory flies. (A) Box plots of phylogenetic diversity (PD tree) and number of observed species of microbiota from laboratory and wild D. suzukii flies. (B) Unweighted and weighted UniFrac-based PCoA plots of bacterial communities in laboratory and wild D. suzukii flies. Statistically significant differences of alpha diversities were analyzed using the Wilcoxon rank sum test. Statistically significant differences in beta diversities were analyzed using Adonis analysis with 999 Monte Carlo permutations. Statistical significance levels are shown in plot figures. ****, P < 0.0001. (C) Taxonomic composition of microbial communities associated with D. suzukii flies. Each bar is indicated by a different color at the genus level (>0.5% of average relative abundance in groups). F, female; M, male. (D) List of isolated culture-dependent microbes from laboratory D. suzukii flies.