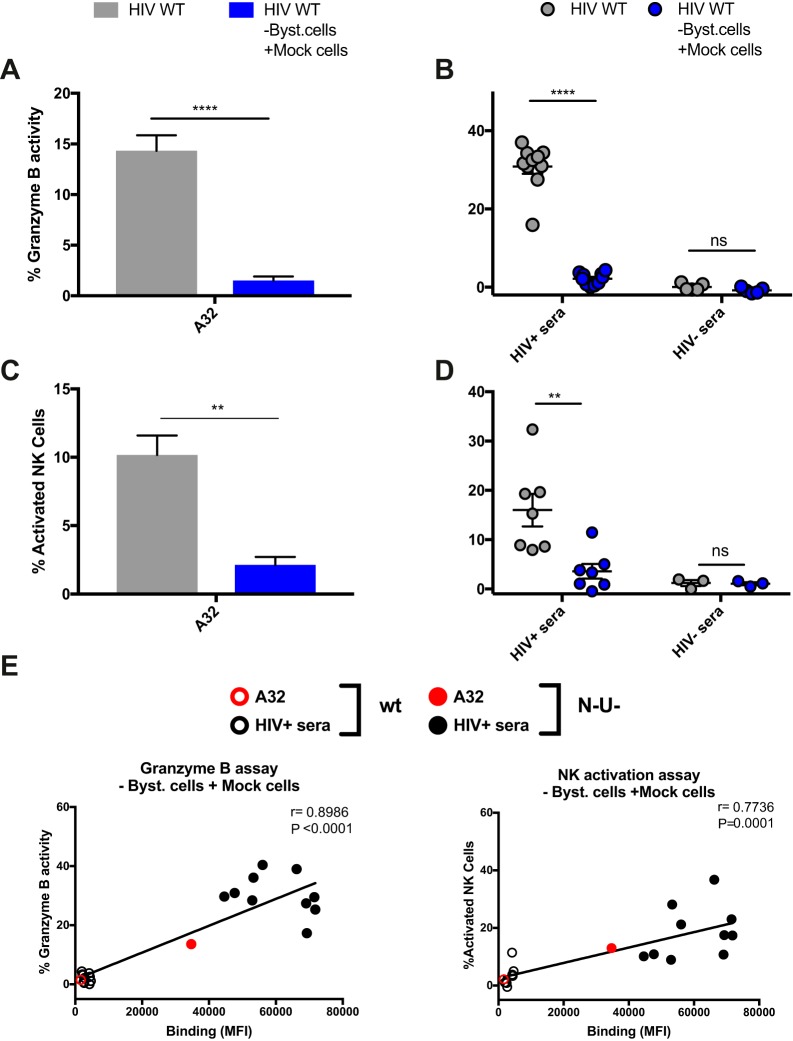
FIG 6 .
Replacement of uninfected bystander cells by autologous mock-infected cells strongly reduces the ADCC responses detected with granzyme B and NK cell activation assays. Primary CD4+ T cells were mock infected (Mock) or infected with the NL4.3 ADA GFP WT virus (HIV WT). Forty-eight hours postinfection, uninfected bystander CD4+ T cells were removed and replaced by the same number of autologous mock-infected cells (HIV WT -Byst. cells +Mock cells) prior to ADCC measurements with the granzyme B assay (A and B) and the NK cell activation assay (C and D). (A and C) ADCC responses detected with A32 (5 μg/ml). (B and D) Responses mediated by HIV+ and HIV− sera (1:1,000 dilution). (E) A correlation between the ability of A32 and HIV+ sera to recognize infected cells and the ADCC responses detected with the granzyme B and NK cell activation assay was observed when the uninfected bystander CD4+ T cells were replaced by autologous mock-infected cells in the context of a WT infection. All graphs shown represent ADCC responses obtained in at least 5 independent experiments. Error bars indicate means ± standard errors of the means. Statistical significance was tested using unpaired t test or Mann-Whitney test (A to D) and a Pearson correlation test (E) (**, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001; ns, nonsignificant).