Fig. 5.
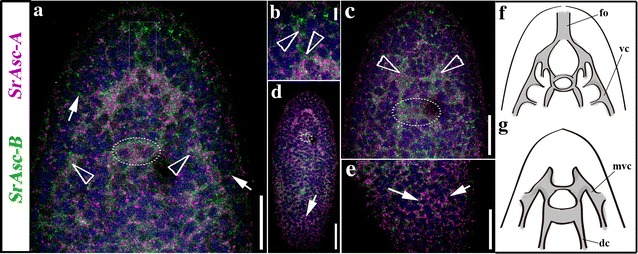
Expression of SrAscA (pink) and SrAscB (green), Achaete-Scute gene family orthologs in (aprox.) 24 h juvenile of the acoel S. roscoffensis. a Double-FISH expression patterns of a medio-ventral frontal section in the anterior part of the animal. Arrowheads indicate the location of cell clusters where the expression is higher within the CNS (also visible in the SrAscB juvenile’s pattern of the Fig. 1). Arrows point to the peripheral nerve tracks connected to the animal’s surface. A rectangular box labels the expression domain of both genes in the area of the statocyst. b Detailed image of the double-FISH-detected domain of expression in frontal organ’s associated cell populations (arrowheads). c Dorso-medial, frontal, section of the double-FISH detecting genes’ expression in the anterior part of the animal. Arrowheads point the location of the two lobes of the brain. The circle surrounds the position of the statocyst. d Dorsal view of a whole mount double-FISH stained animal where it can be appreciated the SrAscA expression in the peripheral nerve net. A circle surrounds the position of the statocyst. The merging of the cords can be detected both anteriorly and posteriorly (arrow). e Detail in a higher magnification image of the posterior part of the organism showed in d, arrows point the posterior end of the cords. f Scheme of the ventral part of the animal, indicating the nervous system structures where the acoel has the expression domains of studied genes. g Scheme of the dorsal part of the animal, indicating the nervous system structures where the acoel has the expression domains of studied genes. fo frontal organ, vc ventral cord, mvc medio-ventral cord, dc dorsal cord. Scale bars a = 20um; b = 5um; c = 20um; d = 30um
