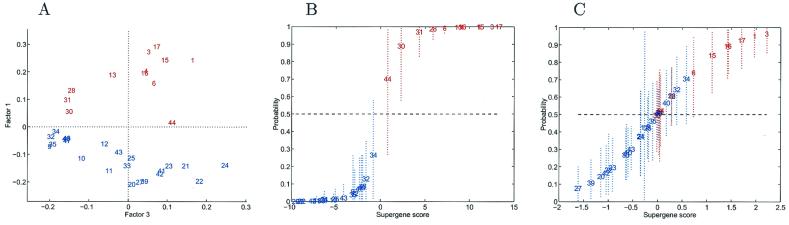
Figure 4.
Analysis for nodal comparisons. (A) Pairwise factor analysis. Breast tumors depicted in a scatter plot on two dominant factors underlying 100 genes selected in pure discrimination according to nodal status. Each tumor is indicated by a simple index number (see Table 2) and is color coded, with red indicating node positive cases with at least three identified positive nodes and blue indicating lymph node negative cases. Factor 1 is clearly discriminatory (Factor 3 is chosen purely for display purposes). (B) One-at-a-time crossvalidation predictions of classification probabilities in nodal analysis. The values on the horizontal axis are estimates of the overall factor score in the regression. The corresponding values on the vertical axis are estimated classification probabilities, with corresponding 90% probability intervals marked as dashed lines to indicate uncertainty about these estimated values. The analysis and predictions for each tumor are based on the screened subset of 100 most discriminatory genes. (C) One-at-a-time crossvalidation predictions in the nodal study, in a format similar to that of A. Each case is predicted only on the basis of the nodal status of the remaining training tumors, with the subset of 100 genes reselected in each case. As such, the analysis exhibits the resulting uncertainties about the extent of true predictive accuracy in a practical setting, reflecting inherent variability due to heterogeneity of expression profiles.