Figure 2.
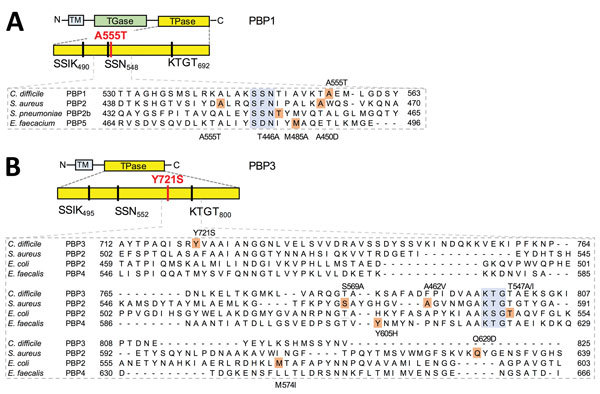
Amino acid substitutions in 2 PBPs predicted to be associated with imipenem resistance in Clostridium difficile, Portugal. The domains and conserved motifs SXXK, SXN, and KTG[T/S] are shown for the following proteins: PBP1 (A), homolog of CDM68_RS04280 of RT017 strain M68 (GenBank accession no. NC_017175) or CD630_07810 in the laboratory strain 630; and PBP3 (B), homolog of CDM68_RS05670 or CD630_11480. The mutations found in these resistant isolates are marked by red lines. The alignments below the 2 proteins show the position (shaded in pink) and nature of the amino acid substitutions observed in the imipenem-resistant RT017 isolates and select PBPs from microorganisms Staphylococcus aureus (GenBank accession no. AAA74375.1), Streptococcus pneumoniae (GenBank accession no. WP_001829432.1), Escherichia coli (GenBank accession no. AAB40835.1), Enterococcus faecalis (GenBank accession no. AAS77615.1), and Enterococcus faecacium (GenBank accession no. AIG13039.1). The conserved motifs in the vicinity of the substitutions are shaded in blue. PBP, penicillin-binding protein; TGase, transglycosylase; TM, transmembrane; TPase, transpeptidase.
