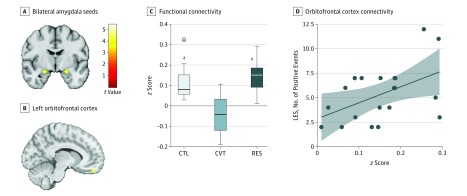
Figure 1. Limbic Network Connectivity.
A, Bilateral amygdala seeds (coordinates in Montreal Neurological Institute space: left: −22, −5, 17; right: 22, −5, 17). B, Region of the left OFC that had greater connectivity with the limbic network (right amygdala seed) in RES as compared with CVT group. Color bar represents t values from the between-group t test (RES>CVT). C, Box-and-whisker plots of amygdala to OFC functional connectivity (quantified as z score) for each group. The horizontal line in the middle of each box indicates the median, while the top and bottom borders mark the 75th and 25th percentiles, respectively. The whiskers above and below the box mark the 90th and 10th percentile. The points beyond the whiskers are outliers. D, Right amygdala to left OFC connectivity plotted against number of LES positive events within the RES group (r18 = 0.48, P = .03). The shaded area represents the 95% CI. CTL indicates control; CVT, converted; LES, Life Experiences Survey; OFC, orbitofrontal cortex; and RES, high-risk resilient.
aP < .001 compared with CVT.