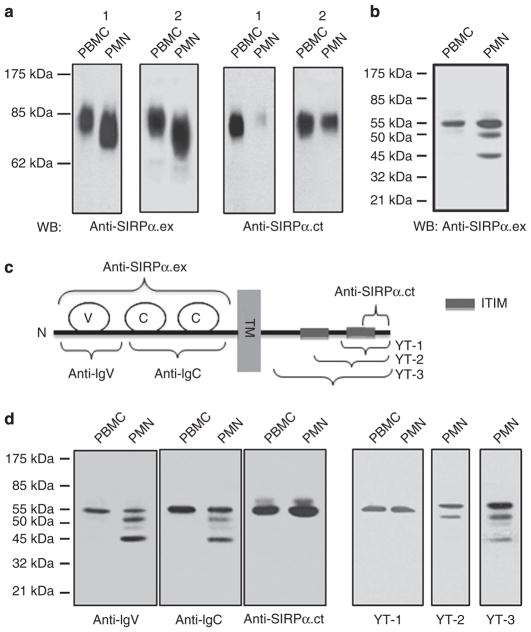
Figure 1. Differential expression of SIRPα in PMNs and PBMCs.
(a) Detection of SIRPα in human PMNs and PBMCs by WB analysis. Freshly isolated human PMNs and PBMCs were lysed and subjected to SDS–PAGE under non-reducing conditions, followed by immunoblotting using antibodies against the extracellular domain (anti-SIRPα.ex) and the C-terminus of the intracellular domain (anti-SIRPα.ct). The figure shows the WB results of PMN and PBMCs obtained from two randomly selected donors (1 and 2). (b) Protein deglycosylation of human PMN and PBMC lysates by PNGase F followed by WB using anti-SIRPα.ex revealed multiple forms of SIRPα in PMNs. (c) Schematic illustration of the epitope regions of SIRPα recognized by the different anti-SIRPα antibodies. The SIRPα protein is shown to contain one IgV-like (V) loop and two IgC-like (C) loops in the extracellular domain. TM, transmembrane domain; ITIM, immunotyrosine-based inhibitory motif; YT-1, 2, 3 are the polyclonal antibodies generated against different regions of SIRPα cytoplasmic tail. (d) WB of deglycosylated PMN and PBMC lysates using different anti-SIRPα antibodies.