Fig. 3.
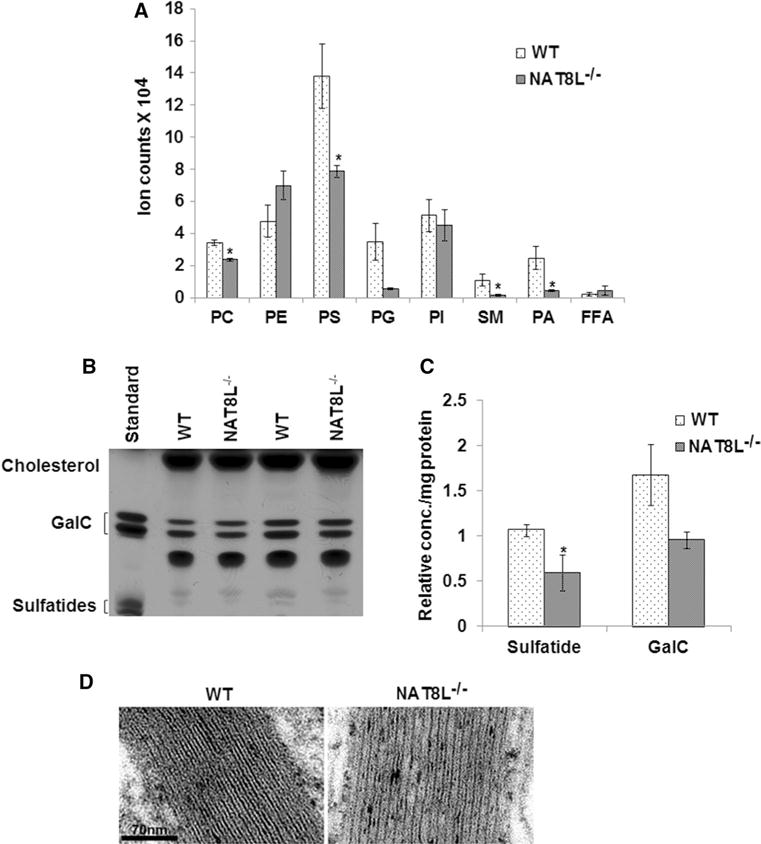
NAT8L−/− mice exhibit changes in myelin lipids and in myelin structure. a Lipidomics data of myelin lipids isolated from 1-year-old NAT8L−/− and wild-type C57Bl/6 control (WT) mouse brains show significant decrease in sphingomyelin (SM), phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylserine (PS), and phosphatidic acid (PA) in NAT8L−/− brains compared to controls. b Representative HPTLC shows bands for the myelin lipids cholesterol, galactocerebrosides (GalC), and sulfatides visualized by copper acetate spray and heating. Lipid standards for GalC and sulfatide were run in the first lane. c After densitometry, sulfatide levels were found to be significantly reduced in myelin isolated from NAT8L−/− mouse brains (n = 3) compared to WT (n = 3). d High-power EM images show less uranyl acetate/lead citrate counterstaining in NAT8L−/− corpus callosum myelin as compared to WT. The intraperiod distances were measured from high-powered images and were found to be significantly increased in the NAT8L−/− mouse (9.50 ± 0.56 nm and 10.95 ± 0.6 in WT and NAT8L−/− mice, respectively), indicating less compact myelin as a result of NAA depletion. Error bars represent SEM. *p ≤ 0.05
