Fig. 1.
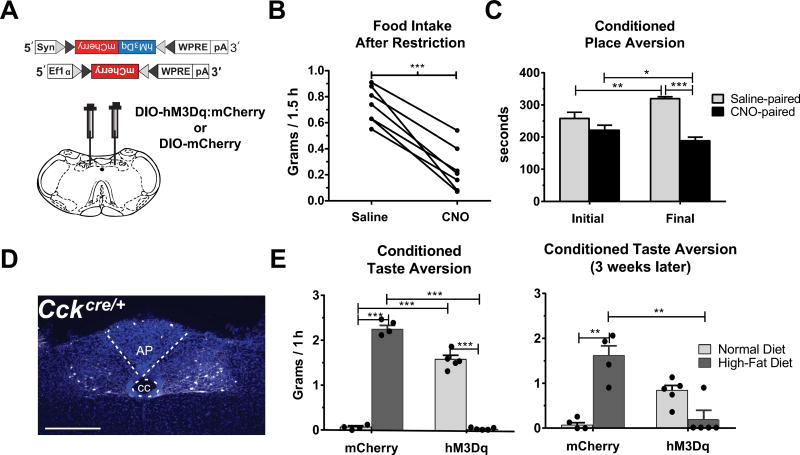
CCKNTS neurons suppress appetite and encode negative valence. (A) Depiction of viral targeting site for the excitatory DIO-hM3Dq:mCherry or DIO-mCherry virus in a coronal section through the medial NTS within the mouse brainstem. (B) In food-restricted animals expressing DIO-hM3Dq:mCherry, activation of CCKNTS neurons with CNO decreased food intake at 2 h compared to intake after saline injection (n = 7). (C) Food-restricted mice expressing hM3Dq in CCKNTS neurons display decreased preference for the CNO-paired side of a box during the final test after conditioning (n = 5). (D) Representative coronal section of the NTS in a CckCre/+ mouse showing viral expression of the hM3Dq receptor in white and DAPI in blue. Scale bar, 100 µm. (E) Mice expressing DIO-hM3Dq:mCherry display CTA and avoided consumption of a high-fat diet that was previously paired with CNO in a choice test two days (left panel) and 3 weeks (right panel) after high-fat diet/CNO pairings (mCherry: n = 4, hM3Dq n = 5). All data represent means ± s.e.m., * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. AP, area postrema; cc, central canal.