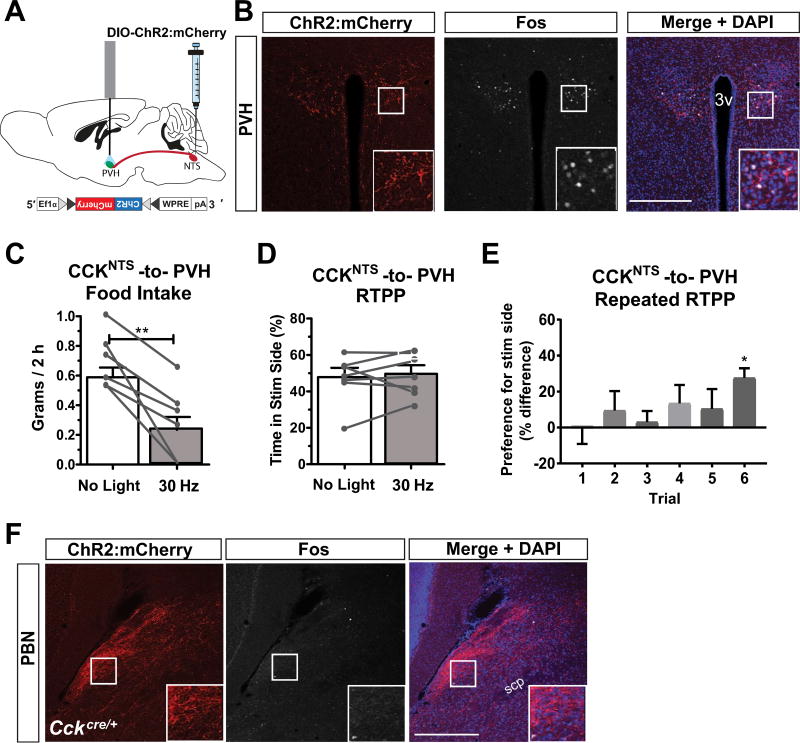
Fig. 3.
A CCKNTS→PVH circuit suppresses appetite and signals positive valence in a repeated RTPP test. (A) Diagram of a sagittal mouse brain depicting site of viral injections and placement of fiber optic cannula for photostimulation of axon terminals in the PVH. (B) Representative immunohistological section demonstrating expression of ChR2:mCherry within fibers and Fos within nuclei in the PVH after 30-Hz photoactivation. (C) 30-Hz photoactivation of CCKNTS axon terminals in the PVH decreased food intake in ChR2:mCherry-expressing mice when measured 2 h after lights out compared to non-stimulated (no light) intake (n = 7). (D) ChR2:mCherry-expressing mice did not display a preference for either side in a single RTPP assay when one side was paired with 30-Hz photostimulation of CCKNTS axon terminals in the PVH (n = 7). (E) After repeated RTPP sessions, animals increased their preference for the side of the chamber paired with photostimulation in the PVH (n = 7). (F) Immunohistological section demonstrating expression of ChR2:mCherry within fibers and absence of Fos immunoreactivity within nuclei in the lateral PBN after 30-Hz photoactivation of PVH afferents. All data represent means ± s.e.m., * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. 3v, 3rd ventricle. Scale bars, 100 µm.