Fig. 1. P2X7 receptor boosts CD39 activity and contributes to NF-κB and STAT3 activation in LPS-primed macrophages.
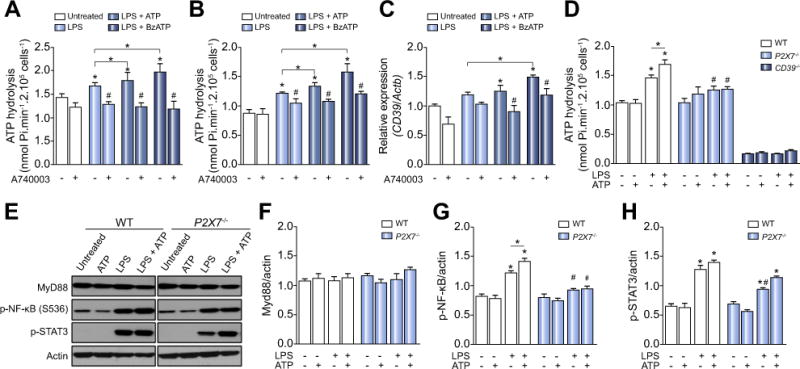
(A) ATP hydrolysis by LPS-primed peritoneal macrophages and (B) BMDM stimulated with P2X7 receptor agonists pretreated or not with A740003. (C) CD39 gene expression in LPS-primed BMDM. (D) ATP hydrolysis by P2X7 and CD39 deficient LPS-primed macrophages stimulated with ATP. (E) Representative Western blot membranes with densitometric analysis of (F) MyD88, (G) p-NF-κB, and (H) p-STAT3 protein expression in LPS-primed macrophages derived from WT or P2X7−/− mice stimulated with 500 μM ATP. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed in triplicates analyzed by one-way ANOVA, Turkey tests. Asterisks represent statistically significant differences (p <0.05; *) compared to unstimulated control group. The number signs (#) represent statistically significant difference (p <0.05) when comparing groups of animals and WT vs. P2X7−/−.
