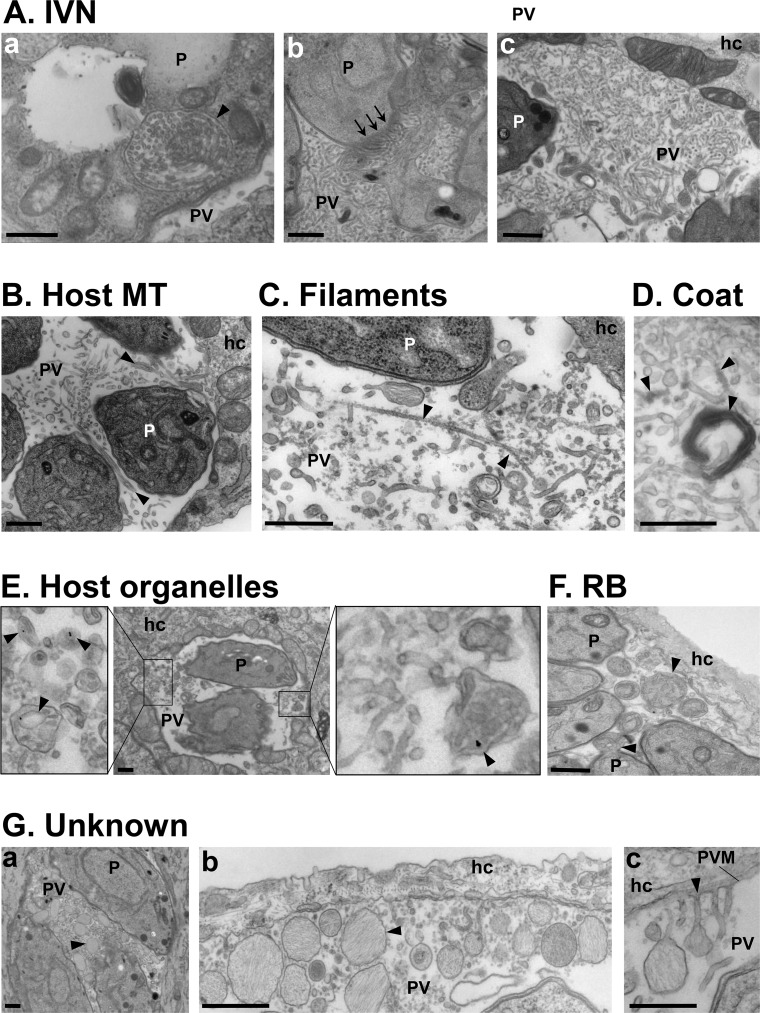
Fig 1. Intraluminal structures in the Toxoplasma PV.
(A-G) Transmission EM of intracellular Toxoplasma. (A) Thin tubules formed by the parasite (P) 20 min post-invasion and packaged within a vesicle (panel a; arrowhead) before being discharged at the basal end of the parasite (panel b; arrows) and spread within the vacuole to form the IVN. (B) Host MT–based invaginations of the PV membrane (arrowheads). (C) Long microfilaments narrower than the IVN tubules (arrowheads). (D) IVN tubules and microtubular structures are coated by e-dense material. (E) Host endocytic organelles containing LDL-gold particles (arrowheads) surrounded by the PV membrane. (F) RB of the mother cells identified by discarded organelles such as the ER, either still attached to daughter cells or free in the PV lumen (arrowheads). (G) Unknown membrane-bound structures containing fibrillary material (arrowheads) accumulated between parasites (panel a), close to the PV membrane (panel b), or appending to the PV membrane (panel c). All scale bars, 500 nm. e-dense, electron-dense; EM, electron microscopy; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; hc, host cell; IVN, intravacuolar network; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; MT, microtubule; P, parasite; PV, parasitophorous vacuole; PVM, parasitophorous vacuole membrane; RB, residual body.