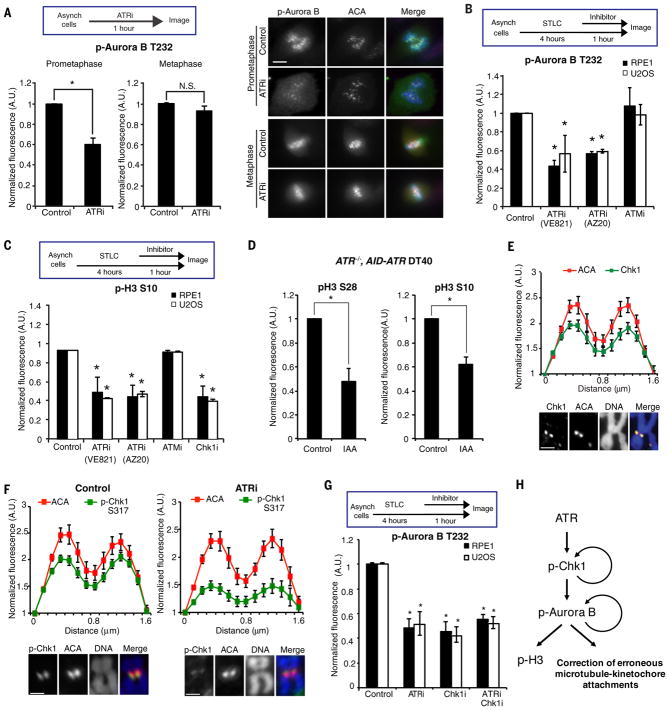
Figure 2. ATR promotes Aurora B activation at centromeres.
(A) Fluorescence intensity of phospho-Aurora B T232 (p-Aurora B) at centromeres in prometaphase or metaphase RPE1 cells untreated or treated with ATRi for 1 h (left). Representative images of untreated and ATRi-treated cells (right). Scale bar, 5 μm. (B–C) Fluorescence intensities of centromeric p-Aurora B (B) and overall p-H3 S10 (C) in S-Trityl L-cysteine (STLC)-arrested prometaphase cells after mock treatments or treatments with the indicated inhibitors for 1 h. (D) Fluorescence intensities of p-H3 S28 and p-H3 S10 in ATR−/−, AID-ATR DT40 cells untreated or treated with IAA for 30 min. (E) Line scan analysis of Chk1 and ACA at centromeres in chromosome spreads of RPE1 cells. Cells were arrested with nocodazole for 5 h. Scale bar, 2μm. (F) Line scan analysis of p-Chk1 and ACA at centromeres in chromosome spreads of RPE1 cells. Cell were arrested with nocodazole for 4 h and then mock or ATRi treated for 1 h. Scale bar, 2μm. (G) Fluorescence intensity of centromeric p-Aurora B in STLC-arrested prometaphase cells after mock treatments or treatments with the indicated inhibitors. Error bars in all panels represent SEM. *P ≤ 0.01, two-tailed t-test. (H) A schema of the ATR-Chk1-Aurora B pathway in mitosis. This pathway is required for full Aurora B activation, which is necessary for H3 phosphorylation and proper kinetochore-microtubule attachment.