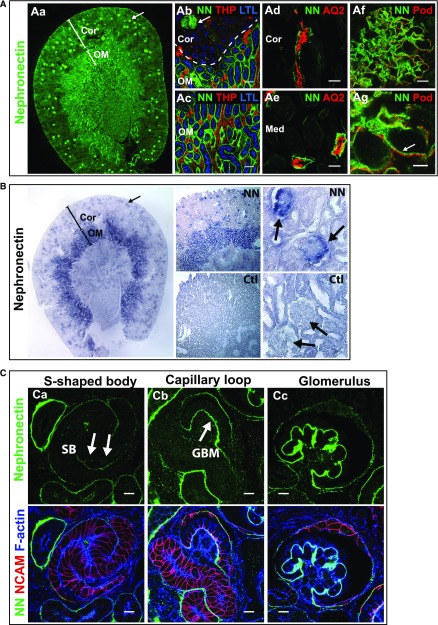
Figure 1.
Nephronectin localizes to glomeruli and renal tubules in mice. (A) Immunolocalization of Npnt in a coronal section of an adult mouse kidney. (Aa) Npnt (NN, green) localizes to glomeruli (arrow) and tubules. The cortex (Cor) and outer medulla (OM) are depicted. At the (Ab) corticomedullary junction and (Ac) outer medulla, Npnt localizes to glomeruli (arrow in Ab), and the basal lamina of proximal tubules marked by apical Lotus Tetragonolubus Lectin (LTL, blue), in the OM but not cortex, indicating it localizes to the S3-segment of proximal tubules. Thick ascending limb tubules are identified by Tamm Horsfall Protein (THP, red). (Ad and Ae) Npnt also localizes to tubules in the (Ad) cortex and (Ae) medulla (Med) that contain Aquaporin 2 (AQ2, red), a marker of collecting ducts. Nephronectin localizes to the GBM in glomeruli (Af and Ag, arrow) adjacent to podocyte foot processes that are marked by podocin (Pod, red). (B) RNA in situ hybridization for Npnt (purple) and control (Ctl, sense probe) in adult kidney shows high expression in glomeruli (arrows) and tubules of the OM, which are likely S3 proximal tubules identified in (A). Staining of glomerular tufts is limited to the outer rims where podocytes reside. (C) Immunolocalization of Npnt in a P0 kidney. (Ca) Low levels of Npnt are found in the primitive nephron tubule, the s-shaped body (SB), including the vascular cleft where the glomerular tuft will develop (arrows). At (Cb) the capillary loop stage and (Cc) in maturing glomeruli, Npnt localizes to the developing GBM. Merge images show NCAM (red), a marker of the developing nephron epithelia, and F-actin (blue) to aid in identification of structures. Scale bars: 50 μm in (Ab and Ac); 20 μm in (Ad and Ae); 10 μm in (Af and C); 5 μm in (Ag). Ctl, control; LTL, Lotus Tetragonolubus Lectin.