Figure 6.
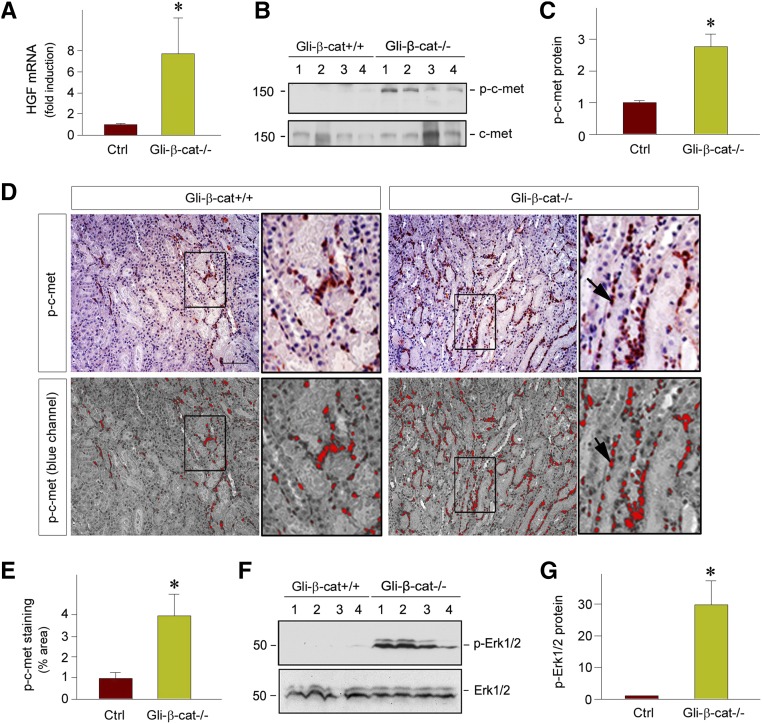
Fibroblast-specific ablation of β-catenin promotes HGF/c-met signaling after AKI in vivo. (A) qRT-PCR revealed an increased expression of HGF mRNA in Gli1-β-cat−/− kidneys at 1 day after IRI, compared with the Gli1-β-cat+/+ controls. *P<0.05 (n=6). (B and C) Western blot analyses show an increased HGF receptor, c-met, phosphorylation at Tyr1234/1235 in the Gli1-β-cat−/− kidneys at 1 day after IRI, compared with the Gli1-β-cat+/+ controls. (B) Representative western blot and (C) quantitative data are presented. Numbers (1–4) indicate each individual animal in a given group. *P<0.05 (n=6). (D and E) Representative micrographs show renal localization of phosphorylated c-met in the Gli1-β-cat+/+ and Gli1-β-cat−/− kidneys at 1 day after IRI. The images in the blue channel were shown in the bottom panels. The phosphorylated c-met protein was detected by immunohistochemical staining. Boxed areas are enlarged. Scale bar, 50 µm. (E) Quantitative data are presented as the percentage of the areas of phosphorylated c-met. *P<0.05 (n=4). (F and G) Western blots demonstrate ERK1/2 phosphorylation in the kidneys of the Gli1-β-cat+/+ and Gli1-β-cat−/− mice at 1 day after IRI. (F) Representative western blot and (G) quantitative data are presented. *P<0.05 (n=4). Ctrl, control.