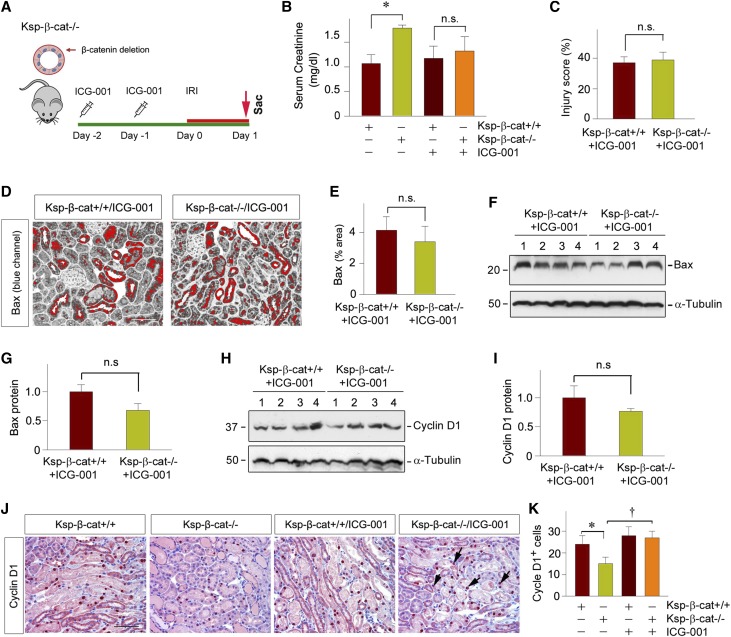
Figure 7.
Pharmacologic inhibition of β-catenin signaling in Ksp-β-cat mice attenuates kidney injury after AKI. (A) Experimental design. ICG-001 was administrated in conditional knockout mice with tubule-specific ablation of β-catenin 2 days before IRI, and the mice were euthanized at 1 day after IRI. (B) Serum creatinine level in Ksp-β-cat+/+ and Ksp-β-cat−/− mice in the absence or presence of ICG-001 at 1 day after IRI. *P<0.05 (n=8–9). (C) Quantitative assessment of renal injury in Ksp-β-cat+/+ and Ksp-β-cat−/− mice after ICG-001 treatments. Injury score (% of injured tubules) is presented (n=4). (D and E) Representative micrographs showed immunohistochemical staining (blue channel) for Bax in the kidneys at 1 day after IRI. Red color indicates Bax-positive tubules. Scale bar, 50 µm. (E) Quantitative data is presented as the percentage of the areas of Bax staining (n=4). (F and G) Western blot analysis showed little difference in Bax expression between Ksp-β-cat+/+ mice and Ksp-β-cat−/− mice administrated with ICG-001. (F) Representative western blot and (G) quantitative data are presented (n=6). (H and I) Western blot analysis demonstrated Cyclin D1 expression also has no changes between Ksp-β-cat+/+ and Ksp-β-cat−/− mice with ICG-001. (H) Representative western blot and (I) quantitative data are presented (n=6). (J and K) Representative micrographs show renal expression of (J) Cyclin D1 in Ksp-β-cat+/+ and Ksp-β-cat−/− mice in the absence or presence of ICG-001. Scale bar, 50 µm. (K) Quantitative data is presented as positive cell number of Cyclin D1 per HPF. *P<0.05; †P<0.05 (n=4). Sac, Sacrifice.