Figure 4. Tuberculosis-related outcomes* in children screened following the WHO symptom-based approach for the management of child contacts, stratified by the HIV-serostatus of the child†.
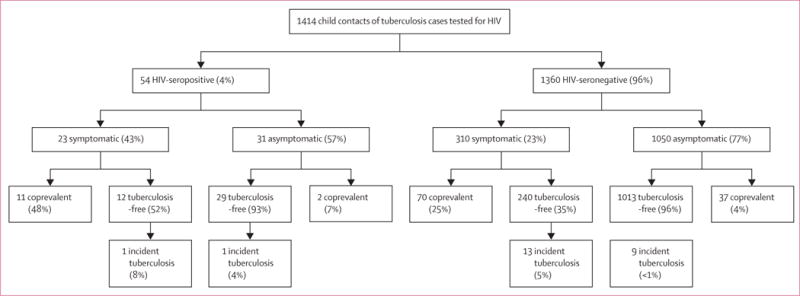
*Individuals with coprevalent disease were excluded from analyses of incident disease. In this figure, tuberculosis-free indicates contacts free of tuberculosis, but these contacts might have had tuberculosis infection. Percentages might not total 100% because within-characteristic percentages were rounded to the nearest integer. †In this flowchart, infants with tuberculosis-related symptoms (including chronic cough, fever, night sweats, haemoptysis, weight loss, and loss of appetite,) were included to be screened in the algorithm. Chronic cough was defined as a continuous, non-remitting cough present for >3 weeks. Fever was defined as body temperature of >38°C for 14 days, after exclusion of common causes such as malaria or pneumonia. Weight loss was defined as reporting of weight loss or failure to thrive with confirmatory evidence from the child’s growth chart. Haemoptysis was defined as the expectoration of blood from the lung airways or parenchyma. Night sweats and loss of appetite were self-reported by children and parents. Asymptomatic contacts included children with cough of <3 weeks’ duration and/or fever of <2 weeks’ duration. This analysis included only 1414 child contacts who took an HIV test. The difference between coprevalent tuberculosis among symptomatic and asymptomatic contacts was statistically different for HIV-seropositive children (48% vs 7%, p<0.0001) and HIV-seronegative children (23% vs 4%, p<0.0001).
