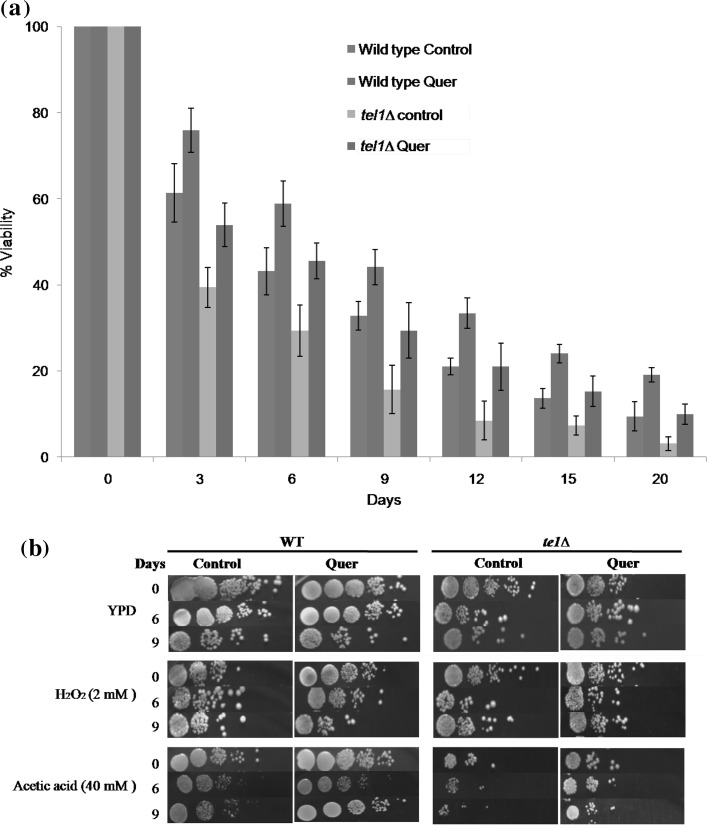
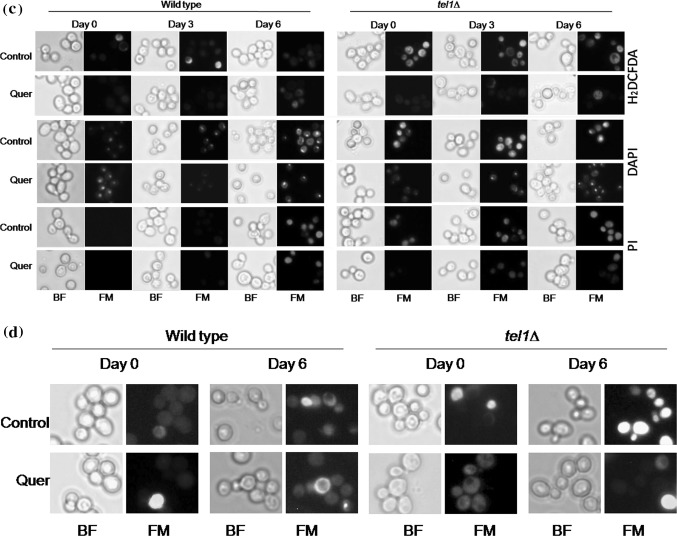
Fig. 4.
Quercetin extends the chronological life span of yeast cells. a Percent viability of wild type and tel1∆ yeast cells during chronological aging. Values are mean ± SD of three independent experiments. b Spot assay. Wild type and tel1∆ cultures from CLS assay were spotted on to YPD plates containing H2O2 (2 mM) and acetic acid (40 mM) and incubated at 30 °C for 2–3 days. Representative images are shown from at least 3 independent experiments. c Detection of ROS, nuclear condensation and plasma membrane integrity staining of Wild type and tel1∆ cells during chronological aging. ROS detection was studied by using a ROS sensing dye H2DCFDA (upper panel), the nuclear condensation was detected by using 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) (middle panel) and plasma membrane integrity was detected by using propidium iodide (PI) (lower panel). Representative images are shown from at least three independent experiments. d AO/EtBr dual staining to detect apoptotic events. Yeast cells were stained with AO/EtBr staining solution as described above. Representative images are shown from at least three independent experiments