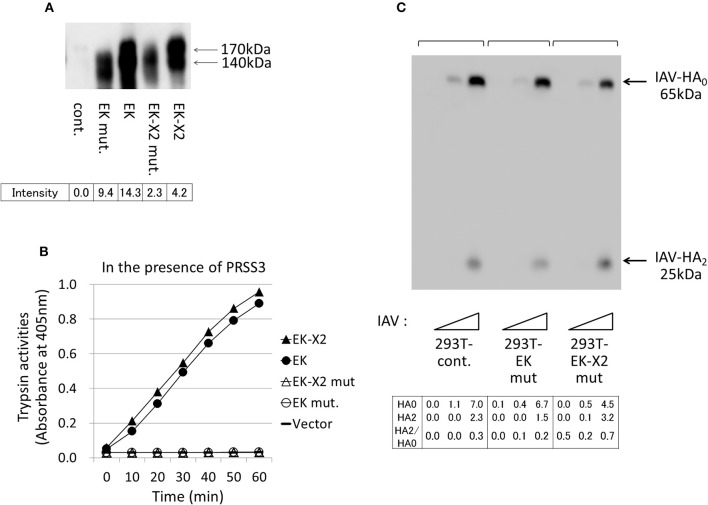
Figure 7.
Protease-deficient mutant EK or EK-X2 has almost no effect on IAV infection. (A) The protease-deficient mutants in which Ala replaced EK Ser971 or EK-X2 Ser1001 in the catalytic triad (H–D–S), as well as wild type EK and EK-X2, were transiently expressed in 293T cells, and the cell lysates were analyzed with western blotting using an anti-EK antibody. The two major protein bands of EK (170 and 140 kDa) and the EK mutant and the slightly larger bands of EK-X2 and its mutant are indicated with arrows, and the band intensities are shown below. (B) The 293T cell lysates transiently expressing wild type EK, EK-X2, or the protease-deficient mutants were mixed with the PRSS3-expressing 293T cell lysate. The amounts of pNA released from the substrate were measured at 405 nm as the trypsinogen-activating function. (C) 293T and mutant EK- or EK-X2-expressing cells (1 × 105 each) were plated in a 24-well plate and inoculated with different amounts of IAV (MOI = 0, 0.001, 0.01 from the left of  ). At 48 h after infection, the same amounts of cell lysates were subjected to electrophoresis and western blotting with an anti-IAV HA antibody. The 65-kDa precursor IAV HA0 and the cleaved 25-kDa C-terminal IAV HA2 fragment are indicated by arrows. The HA0 and HA2 intensities and the HA2/HA0 ratio are shown below.
). At 48 h after infection, the same amounts of cell lysates were subjected to electrophoresis and western blotting with an anti-IAV HA antibody. The 65-kDa precursor IAV HA0 and the cleaved 25-kDa C-terminal IAV HA2 fragment are indicated by arrows. The HA0 and HA2 intensities and the HA2/HA0 ratio are shown below.