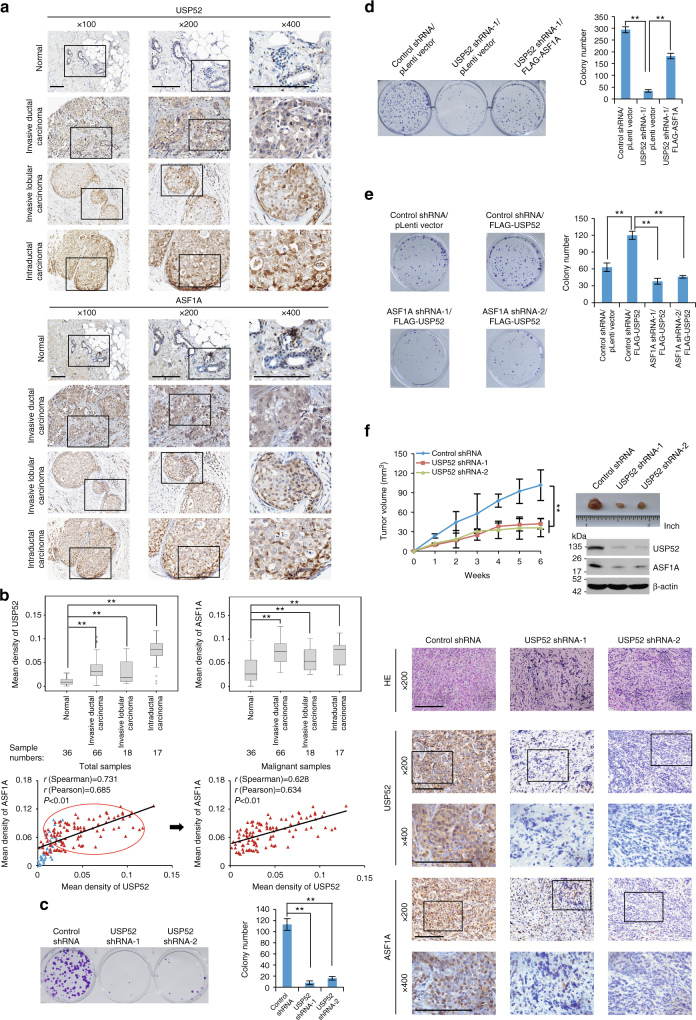
Fig. 6.
USP52/ASF1A signaling axis is implicated in breast carcinogenesis. a Immunohistochemistry analysis of the expression levels of USP52 and ASF1A in different histologic types of breast tumors and adjacent normal mammary tissues. Representative images (×100, ×200, and ×400 magnification) from these samples are shown. Scale bar, 50 μm. b Scores of the stained sections from a were determined by evaluating the intensity of immunopositivity by Image-pro Plus software and are presented with box plots. **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA. The correlation coefficient and P-values were analyzed as indicated. c Colony formation assays of MCF-7 cells stably expressing USP52 shRNAs. Representative images from biological triplicate experiments are shown. **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA. d Colony formation assays of MCF-7 cells stably expressing the indicated genes and shRNAs. Representative images from biological triplicate experiments are shown. **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA. e Colony formation assays of MCF-7 cells stably expressing the indicated genes and shRNAs. Representative images from biological triplicate experiments are shown. **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA. f MCF-7 tumors with the indicated treatments were transplanted onto athymic mice and tumor volumes were measured weekly. Each bar represents the mean ± S.D. for different animal measurements (n = 6). **P < 0.01, two-way ANOVA. The levels of USP52 and ASF1A proteins in these tumors were examined by western blotting and immunohistochemistry analysis. Representative images (×200 and ×400 magnification) are shown. Scale bar, 50 μm