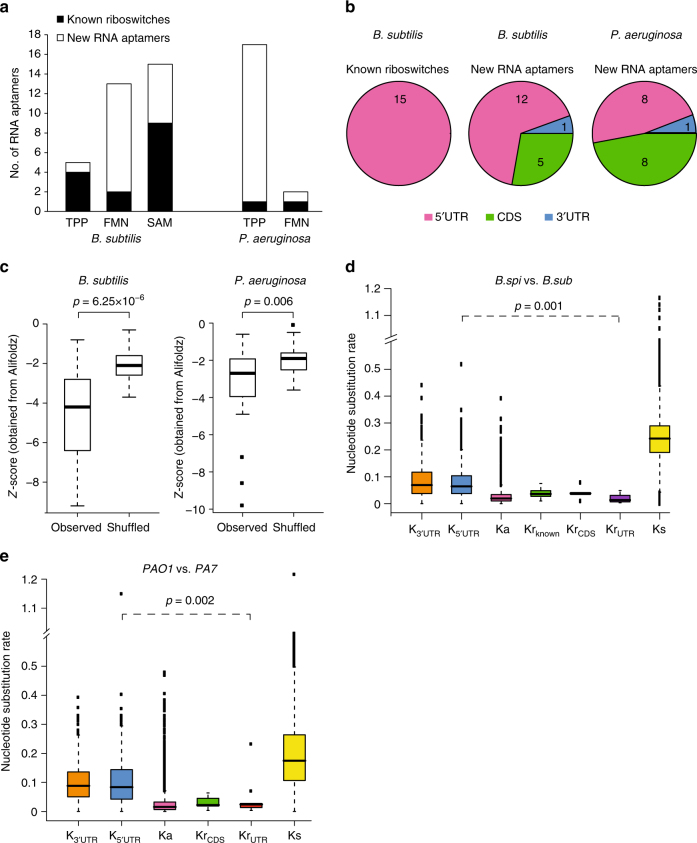
Fig. 2.
PARCEL identifies new RNA aptamers in bacterial species. a PARCEL identifies a total of 52 RNA aptamers in B. subtilis and P. aeruginosa. Black and white bars indicate the numbers of known riboswitches and novel aptamers that are identified in our study, respectively. b Distribution of known riboswitches and new RNA aptamers along the 5′ UTR, CDS, and 3′ UTR regions for B. subtilis and P. aeruginosa, showing that a substantial proportion of RNA aptamers are located in the 3′ UTR and CDS regions. c Comparison of score distribution of Alifoldz12 for RNA aptamers vs. shuffled counterparts. The upper, middle, and lower bounds of the boxplot represent the 75, 50, and 25th percentile of the values, respectively. A negative score indicates a stable, conserved consensus structure. p-value was obtained using the non-parametric Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. d, e Comparison of the nucleotide substitution rate (number of substitutions per base-pair) for new RNA aptamers in coding region (KrCDS), new RNA aptamers in UTR (KrUTR), 3′ UTR (K3UTR), 5′ UTR (K5UTR), synonymous sites (Ks), and non-synonymous sites (Ka). The upper, middle, and lower bounds of the boxplot represent the 75, 50, and 25th percentile of the values, respectively. To calculate nucleotide substitutions, B. subtilis 168 was compared to B. subtilis subsp. spizizenii W23 (d), and P. aeruginosa PAO1 was compared to P. aeruginosa PA7 (e). Note that Krknown denotes the substitution rate of known riboswitches in B. subtilis (15 in total) as annotated in the RegPrecise database11. Krknown was not calculated in P. aeruginosa as there are too few known TPP and FMN riboswitches. p-values were calculated using the non-parametric Kolmogorov–Smirnov test