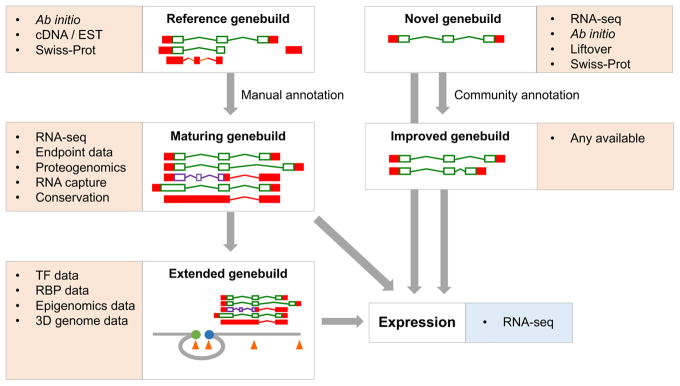
Figure 3. High-level strategies for gene annotation projects.
This schematic details the annotation pathways for reference and novel genomes. Coding sequences (CDS) are outlined in green, nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) is shown in purple and untranslated regions (UTRs) are filled in red. The core evidence sets used at each stage are listed, although their availability and incorporation vary across different projects. The types of evidence used for reference genebuilds have evolved over time: RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) has replaced Sanger sequencing, conservation-based methodologies have become more powerful and proteogenomic datasets are now available. By contrast, novel genebuilds are constructed based on RNA-seq and/or ab initio modelling, in combination with the projection of annotation from other species (known as liftover) and the usage of other species evidence sets. In fact, certain novel genebuilds such as pig and rat now incorporate a modest amount of manual annotation, and could perhaps be described as ‘intermediate’ in status between ‘novel’ and ‘reference’. Furthermore, such genebuilds have also been improved by community annotation; this process typically follows the manual annotation workflows for reference genomes, although at a smaller scale. While all reference genebuilds are ‘mature’ in our view, progress into the ‘extended genebuild’ phase is most advanced for human. A promoter is indicated by the blue circle, an enhancer is indicated by the orange circle, and binding sites for transcription factors (TFs) or RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are shown as orange triangles. Gene expression can be analyzed on any genebuild regardless of quality, although it is more effective when applied to accurate transcript catalogues. Clearly, the results of expression analyses have the potential to reciprocally improve the efficacy of genebuilds, although it remains to be seen how this will be achieved in practice (indicated by ‘?’).