Figure 2. C. jejuni Genomic Variants are Consistently Selected for During Human Infections.
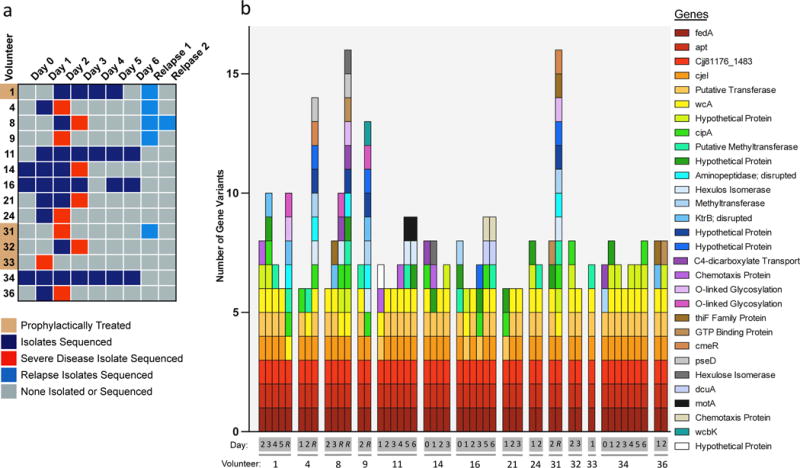
a, Infection populations sequenced. Whole genome sequencing was performed on 49 infection isolate populations, taken from 14 volunteers across 6 days of primary infection. 5 volunteers relapsed after the clinical trial, and those infection isolate populations were also sequenced. Some volunteers experienced severe disease on the noted days (red) and therefore received early antibiotic intervention. Some volunteers received exploratory prophylactic treatment with the antibiotic Rifaximin as noted. Sequencing details are noted in Sup. Fig. 2. b, Genomic variants detected per volunteer isolate population, noted by the genes the variants affect. The number of genomic variants detected per infection population is noted on the y-axis, and the x-axis denotes the day and volunteer the sample was taken from, with R denoting a relapse sample. The corresponding genes are listed by their gene name or annotation when considering homologs across CG8421, 11168, and 81176 C. jejuni strains.
