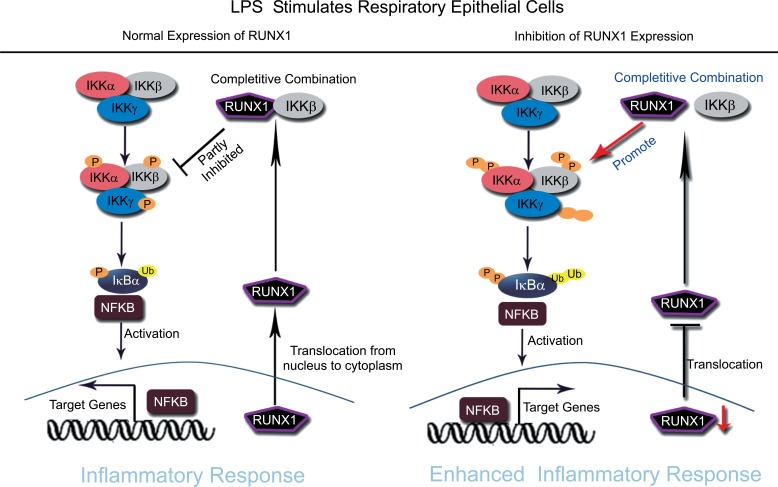
Fig. (2).
RUNX1 acts as a cytoplasmic attenuator of NF-κB signaling in respiratory epithelial cells. After respiratory epithelial cells exposure to LPS, RUNX1, the nuclear transcription factor, translocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, and competitively binds to IKKβ to form complexes, which resulted in partly inhibiting of the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway (left). The loss or inhibition of RUNX1 expression in respiratory epithelial cells can enhance LPS induced inflammatory response by promoting the activation of NF-κB signaling (right).