Figure 2. Probabilistic energy analysis and design rationale for morphable 3D mesostructures.
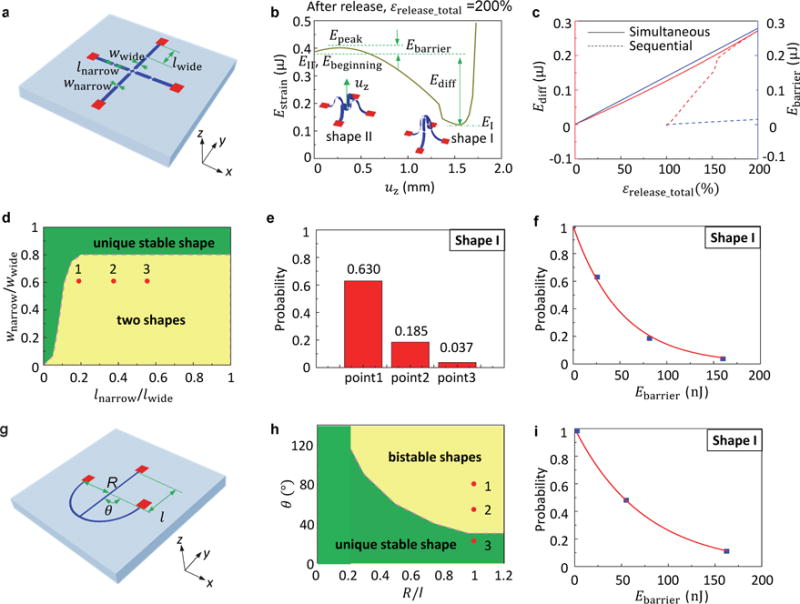
a-f, Analysis for a structure based on a straight ribbon. a, Schematic illustration of a straight ribbon structure. b, Strain energy as a function of out-of-plane displacement for ( ) = (0.77 mm, 0.1 mm, 0.16 mm, 40 μm, 6 μm, 100%) and an elastic modulus of 4.02 GPa. The insets show the stable configurations at the corresponding out-of-plane displacement. Here, l, w and t are the length, width and thickness of the two constituent ribbons, respectively, and the subscripts ‘narrow’ and ‘wide’ denote the creases and other regions, respectively. c, Energy difference and energy barrier versus total release strain for 3D structures that arise from simultaneous and sequential releases. d, Design diagram in the space of length ratio and width ratio. e, Experimentally determined probability for achieving Shape I by sequential release for three different parameter combinations (wnarrow/wwide, lnarrow/lwide)=(0.3,0.2), (0.3,0.4) and (0.3,0.6). f, Dependence of the probability on the magnitude of the energy barrier. g-i, Analysis for the hybrid straight/curved ribbon structure. g, Schematic illustration of a hybrid straight/curved ribbon structure. h, Design diagram in the space of length ratio and arc angle. i, Dependence of the probability on the magnitude of the energy barrier.
