Figure 5.
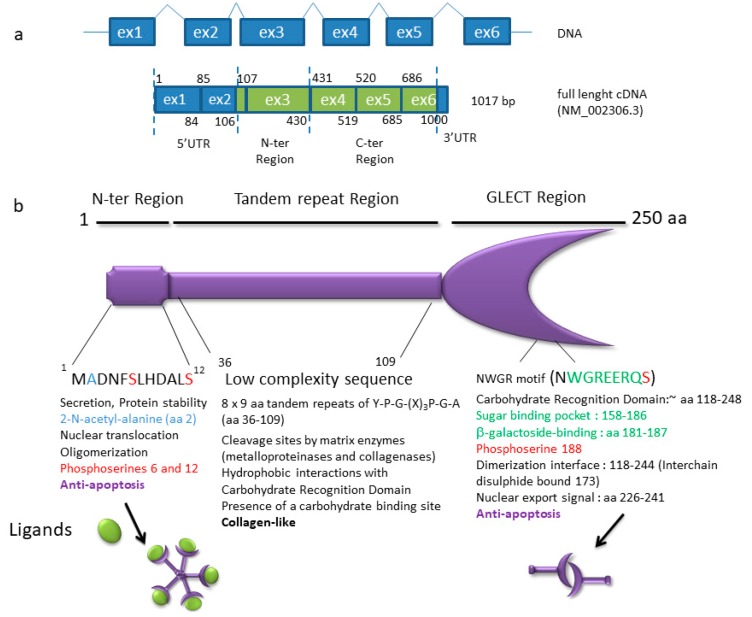
Galectin-3 is an example of a non-classic DNA-binding and RNA-binding protein (DRBP) harboring a large IDR. (a) The LGALS3 gene maps to 14q21-2. Six exons are found in full-length cDNA. In the bottom schema, protein coding sequences are highlighted in green, whereas untranslated exons are depicted in blue. Three alternative spliced variants encode three proteins which are 250 (full-length, shown in b), 223, and 88 amino acids (aa) (not shown), respectively. Four alternative spliced transcripts (not shown) are non-coding RNAs. (b) Functional domains of human galectin-3 (comprised of 250 aa). Galectin-3 is composed of three major domains [127,128]. Two of these domains—the short 12 aa N-terminal region and the 130 aa globular C-terminal domain (118–248 aa) containing the CRD with the carbohydrate binding site (181–187 aa) [119,127] are involved in apoptosis regulation. Galectins are a large family of proteins with a galactose-lectin region (GLECT) containing a common CRD able to bind many glycoprotein and glycolipid targets with β-galactoside motifs. They regulate cell death both intracellularly and extracellularly and have other relatively broad functions. Galectin-3 is the only galectin with both anti-apoptotic and pro-apoptotic activities, according to cell types. This is also the only galectin to harbor a long IDR in its structure, between the N- terminal and C-terminal domains [129]. The galectin-3 IDR is a LC sequence harboring a stretch of repetitions of three aa (proline, glycine, and tyrosine) with a 9 aa collagen-like consensus sequence: Y-P-G-(X)3-P-G-A. This domain (with approximately from 20 to 100 amino acids) interacts with itself and with a part of the CRD not involved in carbohydrate recognition (approximately 200–220 amino acids), forming a fuzzy complex via intermolecular and intramolecular interactions, mainly through hydrophobicity [119]. A new carbohydrate binding site was recently identified in the LC [130]. Like many RBPs, galectin-3 harbors phosphorylable serines (three serines highlighted in red) and is able to constitute multimers (pentamers). The β-galactoside binding motif is in green. Galectin-3 is involved in the mRNA life-cycle through different ways: through binding with the ribonucleoprotein U1 of the spliceosome [131,132], through stabilizing mRNA (through hnRNP-L interaction), and through mRNA nuclear export and storage in cytoplasmic granules [120]. Galectin-3 also acts as a player in the DNA damage response through its interaction with BARD1 in a large complex involving a BRCA1/BARD1 heterodimer [126]. Galectin-3 interacts in an O-GlcNAcylation-dependent manner with a key mitotic regulator, the nuclear mitotic apparatus protein (NuMA), which is required for the establishment and the cohesion of the mitotic spindle [125]. The subdomains or motifs involved in DRBP functions which are newly attributed to galectin-3 have not been identified yet.