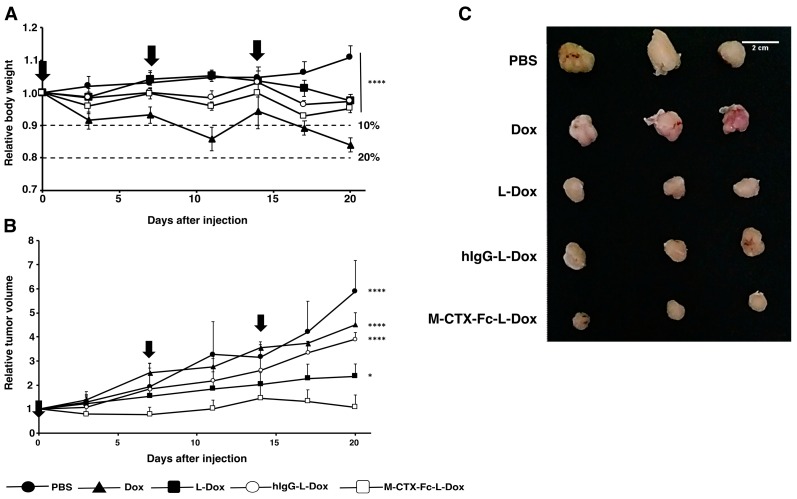
Figure 8.
M-CTX-Fc-L-Dox suppressed tumor growth in the most effective manner in vivo. (A) The relative body weight of mice bearing tumors during the treatment. M-CTX-FC-L-Dox and other liposome formulations were less toxic than naked doxorubicin. The statistical significance in mean values of more than two groups was determined using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post hoc Tukey HSD were applied using relatives body weight of Dox treatment as control. ****, p < 0.001. (B) The effect of different formulations of doxorubicin on the volume of tumors. M-CTX-Fc-L-Dox was the most effective formulation to suppress the growth of tumor. Doxorubicin in each formulation was administered at 7-day intervals (indicated by vertical arrows). The statistical significance in mean values of more than two groups was determined using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and post hoc Tukey HSD were applied using relatives tumor volume of M-CTX-Fc-L-Dox treatment as control, *, p < 0.05; ****, p < 0.001 (C) The tumors from the experiment (B) representing each group were displayed exhibiting the effect of each formulation of doxorubicin. Data are expressed as the mean with ±SD where n = 3.