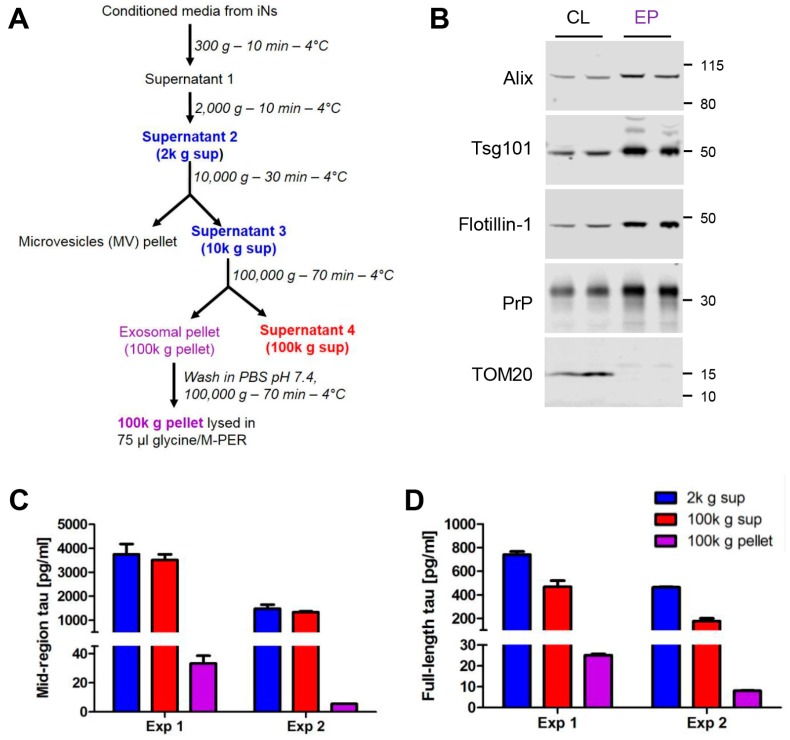
Figure 3.
Exosomes from human iPSC-derived neurons contain detectable levels of full-length, aggregation-competent tau. (A) Flow chart describing the centrifugation procedure used to isolate exosomes from conditioned medium (CM). The speed, duration and temperature of each centrifugation step are indicated to the right of the arrows. Immediately after collection, CM was centrifuged at 300× g to remove dead cells and then 2000 g to remove cellular debris. The clarified CM was then centrifuged at 10,000× g to pellet microvesicles. The resulting supernatant (S3) was centrifuged at 100,000× g for 70 min to pellet exosomes, and these were washed once in PBS. The wash supernatant was discarded and the final exosomal pellet was lysed in glycine/MPER buffer. CM from two separate iN cultures, designated Experiment (Exp) 1 and Exp 2, was collected and processed as described. A portion of exosomal pellet (EP) lysate was analyzed by Western blotting alongside thecell lysates (CL) of iNs from which the exosomes were derived (B). Antibodies used are indicated on the left and the migration of molecular weight standards (in kDa) is on the right. Tau was measured in CM (2000 g (blue) and 100,000 g (red) supernatants and the lysed 100,000 g exosome pellet (purple) using our mid-region (C) and full-length (FL) (D) ELISAs. Concentrations represent the amount of analyte present in 1 mL of starting iN CM and account for dilution and concentration steps. Results for each culture (Exp 1 and 2) represent mean ± SD of technical triplicates.