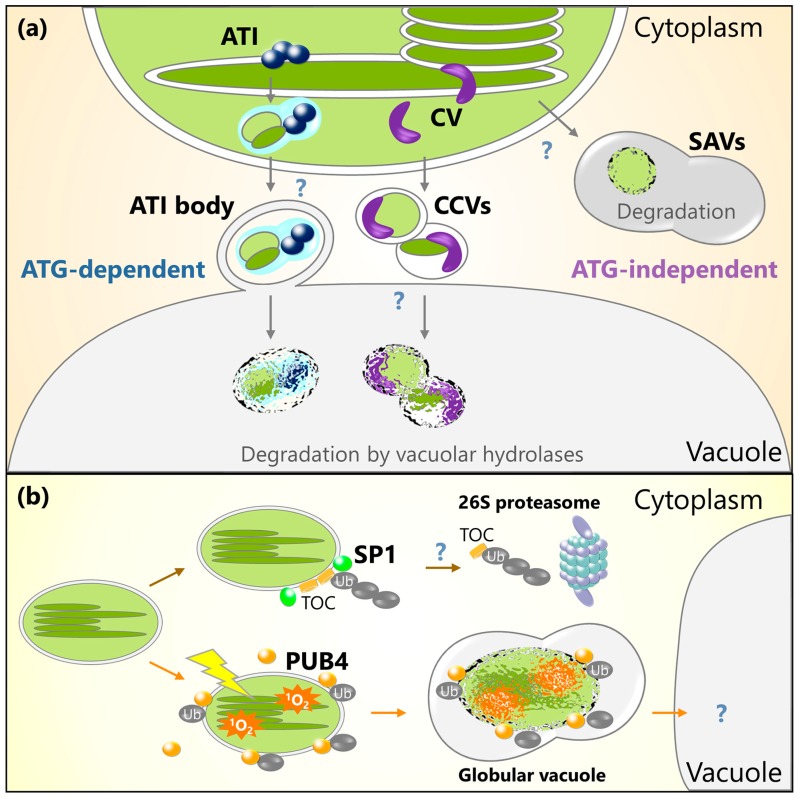
Figure 2.
Schematic model for chloroplast protein turnover mediated by ATI bodies, CV-containing vesicles (CCVs), senescence-associated vacuoles (SAVs), or ubiquitination. (a) Plastid-associated ATI bodies are produced in chloroplasts and are then delivered into the central vacuole via an autophagy-dependent pathway. ATI bodies transport thylakoid, stroma, and envelope proteins. CV protein also interacts with thylakoid and stroma proteins, and then induces the production of CCVs that transport thylakoid, stroma, and envelope proteins into the central vacuole via an autophagy-independent pathway. SAVs are small lytic compartments that form in the cytoplasm. Stroma components are incorporated into the SAVs for digestion. (b) Chloroplast outer envelope-anchored E3 ligase, SP1, ubiquitinates TOC proteins and facilitates their degradation by 26S proteasome. Cytoplasmic E3 ligase PUB4 ubiquitinates oxidative chloroplasts accumulating 1O2 for the digestion of such chloroplasts in their entirety.