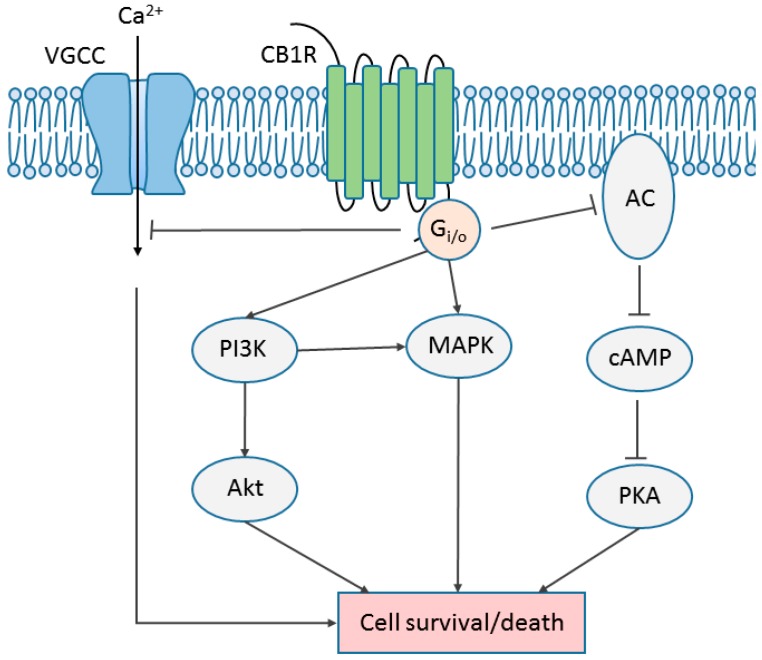
Figure 4.
CB1R-modulated major signaling pathways. Typically, the CB1R is coupled to Gi/o and inhibits the activity of adenylyl cyclase (AC), formation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), and the activity of protein kinase A (PKA). Under certain circumstances, the CB1R can switch its coupling of G protein from Gi/o to Gs or Gq. The CB1R is able to suppress calcium influx via voltage-gated calcium channel (VGCC). Several mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), including ERK1/2, p38, and JNK, are activated by the CB1R. The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) pathway is activated by CB1R as well. Depending on the ligand and subcellular environment, the outcome of CB1R-mediated signaling could be promotion of cell survival or cell death. Arrows indicate stimulation; blunted arrows indicate inhibition.