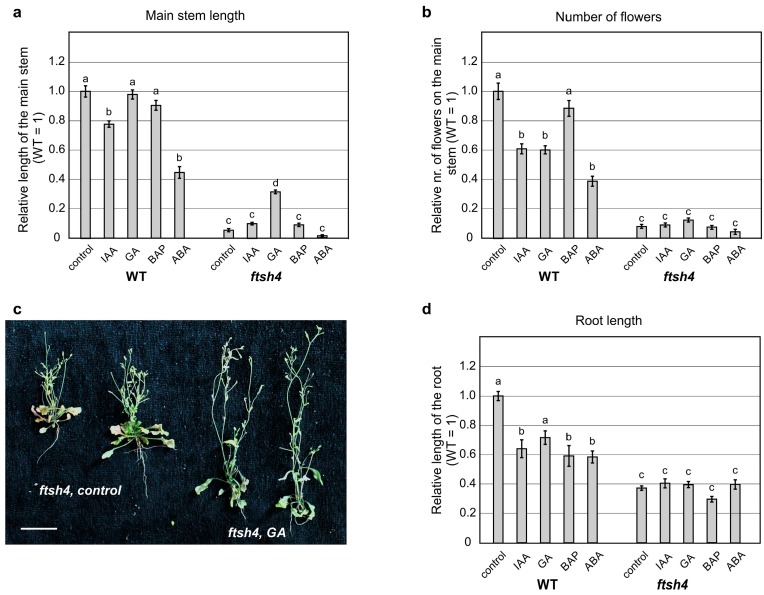
Figure 3.
Lack of responsiveness to exogenous hormones in the shoots and roots of the ftsh4-1 mutants grown at 30 °C. (a,b) Height of the main inflorescence (a) and the number of flowers on the main inflorescence (b) of wild-type (WT) and ftsh4-1 mutant plants grown under long day photoperiod (LD) conditions at 30 °C. The results are expressed relative to the WT control sample (plants without exogenous hormone application). Average values for WT control plants are as follow: main stem length 35.6 mm, number of flowers 21. The main inflorescence height of the ftsh4-1 mutants increases after gibberellic acid (GA3) application (a), but the number of flowers is not significantly changed (b). Mean values (±SE) are shown; (c) the phenotype of adult (when rosette leaves are drying) ftsh4-1 mutant plants grown under LD conditions at 30 °C. ftsh4-1 mutants without exogenous hormone application are shown on the left, and those after gibberellic acid application are shown on the right. Scale bar: 20 mm; (d) the length of the main root of WT and ftsh4-1 mutant plants, grown under LD conditions at 30 °C. Seeds were germinated and grown for three days at 22 °C, transferred to 30 °C to continue the growth for six days and then analyzed. The results are shown relative to the WT control sample (without exogenous hormone application). Mean values (±SE) are shown and significant differences in the WT and ftsh4-1 mutant plants after various hormones application in comparison to their control plants (WT or ftsh4-1), at p < 0.05, are indicated with different letters: a and b between treated and not-treated WT plants; c and d between treated and not-treated ftsh4-1 plants.