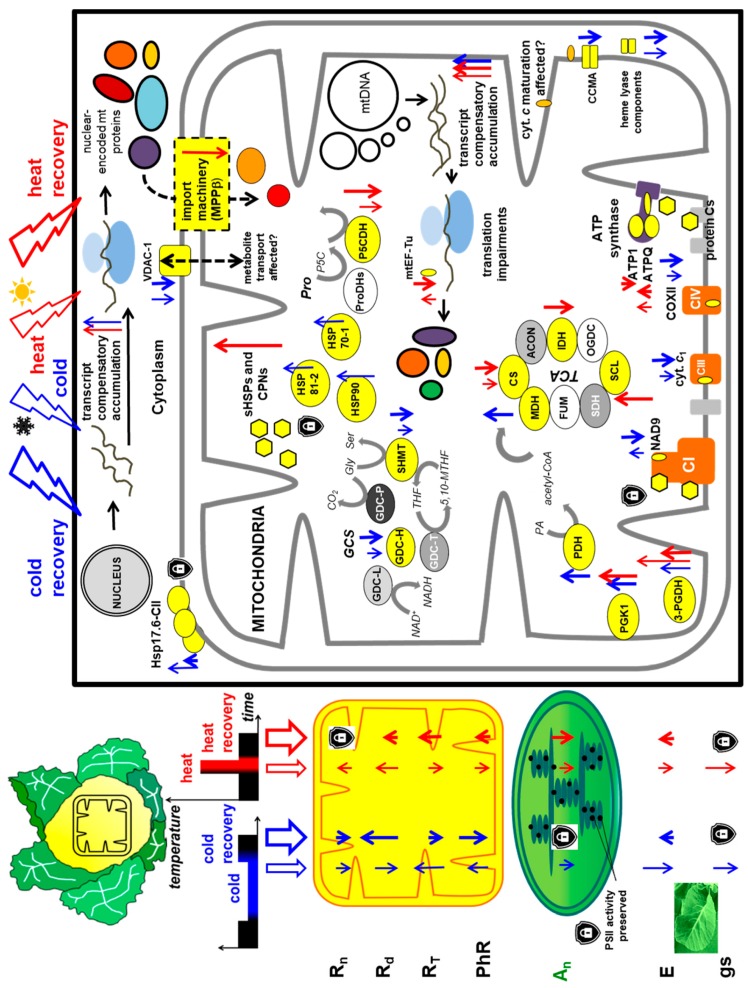
Figure 8.
Proposed model of the impact of temperature stress and recovery on mitochondrial biogenesis in cauliflower curds. Investigated phenomena are depicted. Regulations in the cold and heat are shown by thin blue and red arrows; regulations in stress recovery by the respective thick blue and red arrows. Up-regulations and down-regulations are denoted by arrow heads raised up and down, respectively. Icons with a shield inside depict sustained physiological parameters or phenomena (left panel) or protective function of selected proteins in mitochondrial biogenesis (right panel). Left panel: stress dosage scheme and regulations in key physiological parameters. Right panel: Proteins and complex subunits regulated by abundance are yellow-marked. Some regulatory steps affected by stress conditions are highlighted by discontinuous lines and arrows. Important abbreviations: A, net photosynthetic rate; ATP1, ATPQ, ATP synthase subunits 1 and d; CCM, cytochrome c maturation; CPN, chaperonin; C(s), complex(es); COX, cytochrome c oxidase; CS, citrate synthase; cyt. c, cytochrome c; E, leaf transpiration; GCS, glycine cleavage system; GDC, glycine decarboxylase; gs, stomatal conductance; HSP(s), heat shock protein(s); IDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; MDH, malate dehydrogenase; MPP, mitochondrial processing peptidase; mt, mitochondrial; NAD9, complex I subunit 9; P5CDH, 1-Δ-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; 3-PGDH, 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase; PGK1, phosphoglycerate kinase isoform 1; PhR, photorespiration; ProDH(s), proline dehydrogenase(s); Rd, light respiration; Rn, dark respiration; RT, total light respiration; SCL, succinyl-CoA ligase; SHMT, serine hydroxymethyltransferase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; VDAC, voltage-dependent anion channel. Further data in the text.