Fig. 4.
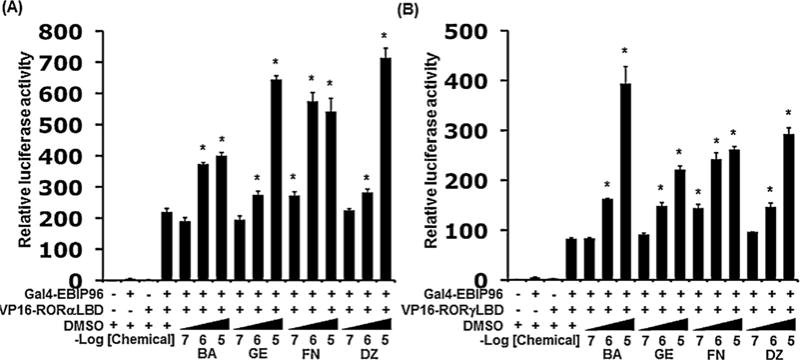
Effects of isoflavones on interactions between ROR-LBD and the co-activator LXXLL peptide in mammalian two-hybrid assays. The analysis was performed by co-transfecting CHO-K1 cells with a pGL4.27-(UAS)5 reporter plasmid, pCMV-β-Gal pM-EBIP96 peptide, and either VP16-RORα(LBD) (A) or VP16-RORγ(LBD) (B). Cells were treated in the presence of the vehicle (DMSO), or increasing concentrations of the four isoflavones as indicated. After 24 h, relative LUC activity was determined as described in Section 2. The firefly luciferase activity was normalized against β-galactosidase activity. BA, GE, FN, and DZ represent each isoflavone, biochanin A, genistein, formononetin, and daidzein, respectively. Values represent the means ± SEM (n = 3) and are presented as the mean n-fold induction over the vehicle control. Significant differences from the vehicle control (DMSO) are indicated by asterisks (*P < 0.05; 1-way ANOVA).
