Fig 1. HMGB1 is concentrated in mouse plasma microvesicles (MVs), but not vesicle depleted plasma up to 72 hours after burn injury.
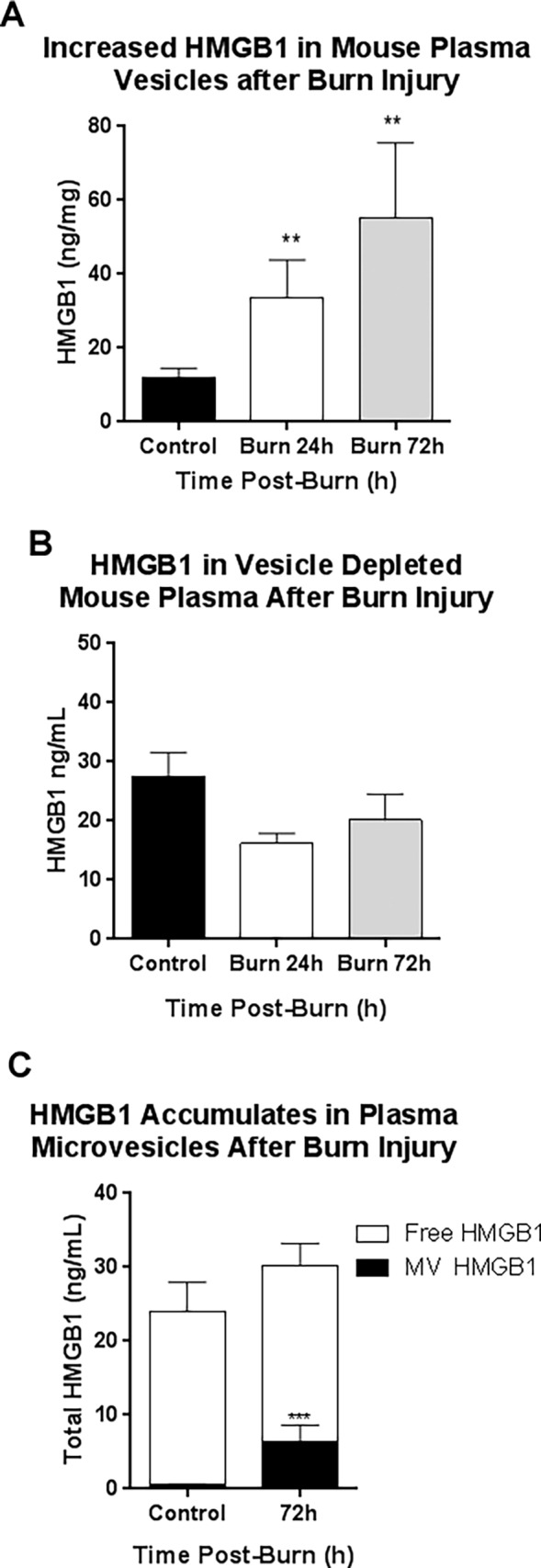
Mice underwent a 20% TBSA thermal injury and were sacrificed at either 24 or 72 hours post-burn. Plasma microvesicles (MVs) were isolated from by sequential centrifugation. HMGB1 levels were assessed by ELISA in the MVs and MV-depleted plasma. (A) HMGB1 was increased in plasma MVs up to 4.6-fold after burn injury. This was observed at 24 hours post-burn (33.6±10.2 vs. 12.06±2.43 ng/mg total protein, mean±SEM, Burn vs Control, **p<0.01,) and at 72 hours post-burn (55.35±20.23 vs. 12.06±2.43 ng/mg total protein, Burn vs Control, mean±SEM, **p<0.01) N = 13 control and 5–6 burn mice per group. (B) HMGB1 levels were not increased in the MV-depleted plasma (C) Analysis of plasma fraction, MV versus MV free plasma, showed that plasma HMGB1 increases at 72 hours were due to increases in MV fraction.
