Figure 5. Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization Induces ELANE Release into the Cytosol and the Subsequent GSDMD Cleavage.
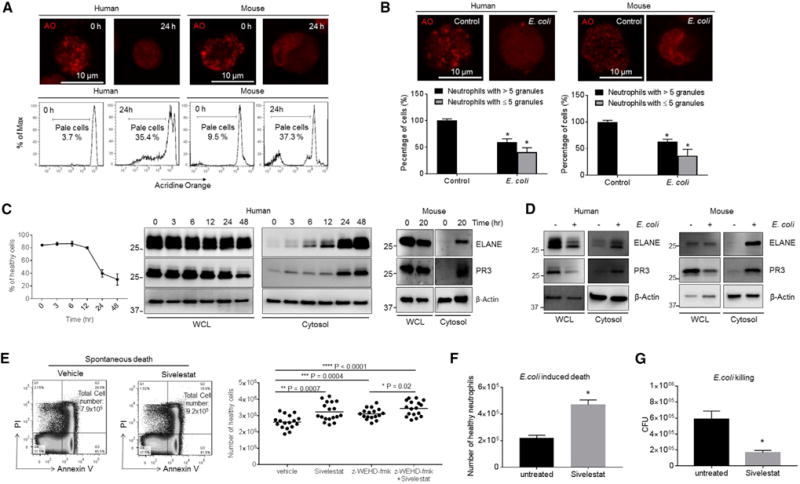
(A) Neutrophil lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP) was assessed using the acridine orange (AO) uptake assay after 24 hr of culture. Shown are representative images and FACS plots of three independent experiments.
(B) E. coli-induced LMP. Mouse or human neutrophils were cultured with opsonized E. coli (1:5 ratio) for 30 min. Cells containing ≥5 granules and cells containing <5 granules are calculated. Shown are representative images of three independent experiments.
(C) PR3 and ELANE protein expression in whole-cell lysates (WCL) and the cytosolic fraction of fresh and aging neutrophils. Shown are representative blots of three independent experiments.
(D) PR3 and ELANE protein expression in neutrophils treated with E. coli. Human and mouse neutrophils were cultured with opsonized E. coli (1:5 ratio) for 60 min. Shown are representative blots of three independent experiments.
(E) Spontaneous neutrophil death in the presence of ELANE, caspase-1/4/5-specific inhibitors, or all of these. Human primary neutrophils were isolated and cultured in the presence of ELANE-specific inhibitor sivelestat (1 μg/mL), caspase-1/4/5-specific inhibitor z-WEHD-fmk (10 μM), or all of these for 26 hr. All of the values represent means ± SDs.
(F) E. coli-induced neutrophil death in the presence of ELANE inhibitor. Human neutrophils were cultured with opsonized E. coli (1:5 ratio) in the presence of sivelestat (1 μg/mL) for 60 min. All of the values represent means ± SDs of three experiments.
(G) In vitro killing of E. coli by aged human neutrophils. Human primary neutrophils were isolated and cultured in the presence of ELANE-specific inhibitor sivelestat (1 μg/mL) for 26 hr. The cultured aged neutrophils were then incubated with E. coli for 1 hr. In vitro bacterial killing capabilities were reflected by the decrease in CFU after indicated incubation periods.
All of the values represent means ± SDs of three experiments. *p < 0.05 versus control.
