Figure 4.
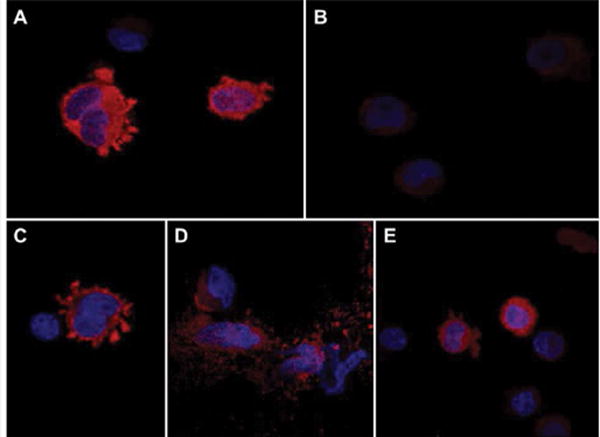
Effects of S/T→A mutations on ASPH protein expression and subcellular localization: PNET2 cells were transiently transfected with wildtype (WT) or a pointmutated (M#:S/T→A) N-Myc-ASPH cDNA. Myc-empty vector (EV) served as a negative control. The M19-H675Q mutant, disrupting ASPH’s catalytic activity, served as a positive control. Representative results obtained by immunofluorescence staining and confocal imaging of cells transfected with (A) WT, (B) M7-S24A, (C) M18-T748A, (D) M19-H675Q, or (E) EV and stained by immunofluorescence with anti-Myc. Immunoreactivity was detected with biotinylated secondary antibody and Streptavidin-conjugated Dylight 547 (red). Cells were counterstained with DAPI (blue). (Merged images: 600× magnification, 2× digital zoom).
