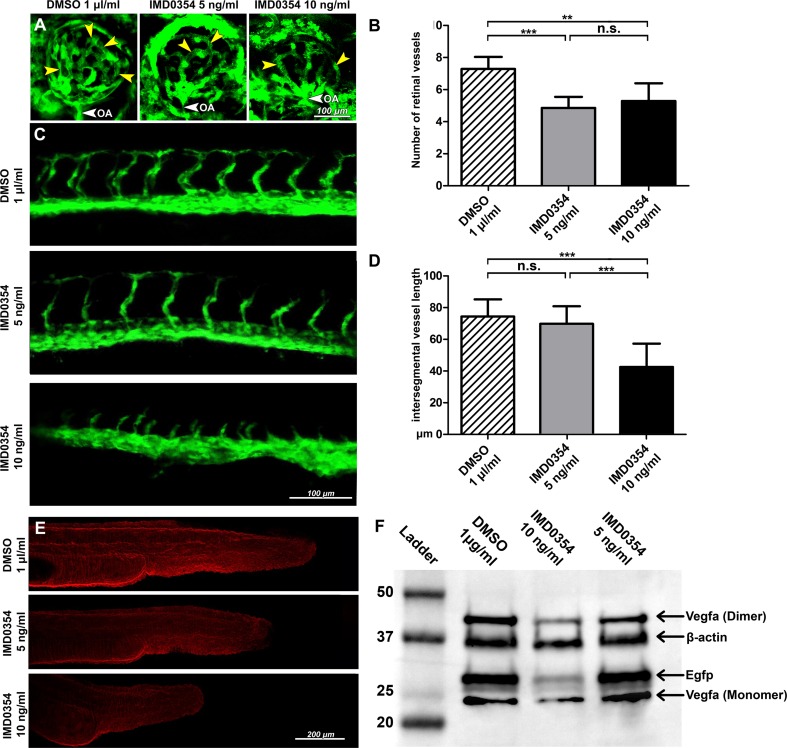
Fig. 5.
Development of retinal, intersegmental vasculature and expression of Vegf-a and EGFP in 24 h post-fertilization (hpf) Tg(fli1:EGFP)y1 zebrafish embryos treated with IMD0354. a Detection of EGFP signal from Tg(fli1:EGFP)y1 transgenic zebrafish embryos retinal vasculature at 72 hpf treated with DMSO or IMD0354 (5, 10 ng/ml). Yellow arrows indicate the retinal vessels. White arrow indicates OA (optic artery). b Quantification of the number of retinal vessels at 72 hpf with DMSO or IMD0354 treatment (5 and 10 ng/ml); (n = 7) One-way ANOVA test with Tukey multiple comparisons was used to determine statistical significance. c Detection of EGFP signal from Tg(fli1:EGFP)y1 transgenic zebrafish embryos intersegmental vasculature at 28 hpf treated with DMSO or IMD0354 (5 and 10 ng/ml). d Quantification of intersegmental vessel length (n = 16) One-way ANOVA test with Tukey multiple comparisons was used to determine statistical significance. e Immunofluorescent detection of Vegf-a (red) expression in zebrafish embryos at 24 hpf. f Western blot analysis of Vegf-a (monomeric and dimeric forms) and Egfp expression in the whole lysate of Tg(fli1:EGFP)y1 transgenic zebrafish embryos at 24 hpf, incubated with DMSO and IMD0354 (10 and 5 ng/ml). β-Actin as the loading control. n.s. p > 0.05; ***p < 0.001