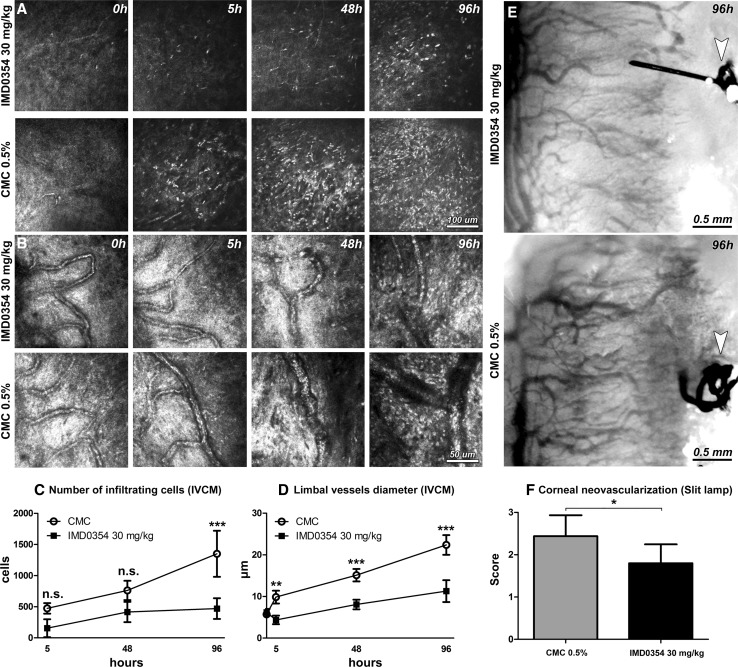
Fig. 6.
In vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM) of rat cornea after induction of corneal neovascularization by suture placement. IVCM images depicting corneal stromal inflammatory cell infiltration (a) and limbal vessels (b) in sutured rat corneas at 0, 5, 48 and 96 h. Quantification of infiltrating cells (c) and limbal vessel diameter (d) in a 400 × 400 μm area (n = 8 animals/time point for both). Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni comparison was used to determine statistical significance. Slit-lamp images of neovascularization of sutured rat corneas at 96 h, treated either with IMD0354 30 mg/kg or CMC (control) (e). The arrows point to the suture placed into the cornea. Semi-quantitative vascular density and vascular progression score (f). (n = 5 IMD0354 treated; n = 8 CMC control group). Student’s t test was used to determine statistical significance. n.s. p > 0.05; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001