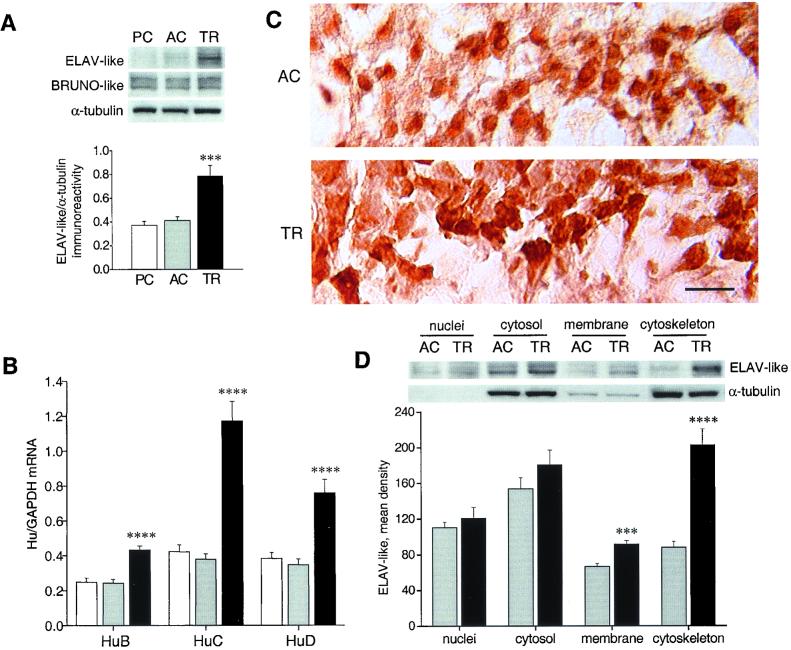
Figure 1.
Up-regulation of neuronal ELAV-like gene expression in mouse hippocampi after radial arm maze training. (A) (Upper) Representative Western blots showing whole-cell lysate immunoreactivity of the ELAV-like and BRUNO-like proteins (using the 16A11 and 3B1 mAbs, respectively) in the passive control (PC), active control (AC), and trained (TR) mouse groups. (Lower) Average results (means ± SEM) for ELAV-like proteins normalized to α-tubulin (n = 5 for each group; ***, P < 0.005, post hoc analysis between AC and TR mice). (B) Determination of the steady-state levels of HuB, HuC, and HuD mRNA by external standard-based, real-time quantitative RT-PCR. The values obtained from hippocampal RNA preparations of the three groups of mice (white bar, PC; light gray bar, AC; black bar, TR) have been normalized to the level of GAPDH mRNA and expressed as means ± SEM (n = 6 for each group; ****, P < 0.001, post hoc analysis between AC and TR mice). (C) Representative images showing the distribution of ELAV-like immunostaining for AC and TR animals in the pyramidal layer of the CA3 hippocampal subregion. (Scale bar, 25 μm.) (D) Representative Western blots (Upper) and average ELAV-like protein levels (Lower) after tissue fractionation. α-Tubulin levels are shown as a control of the nucleocytoplasmic separation, and ELAV-like protein levels are reported as means ± SEM (n = 6 for each group, ***, P < 0.005; ****, P < 0.001, Student's t test). All experiments were repeated at least three times for each hippocampal tissue sample. For statistical analysis, values were subjected to one-way ANOVA and a post hoc Tukey's test unless stated otherwise.