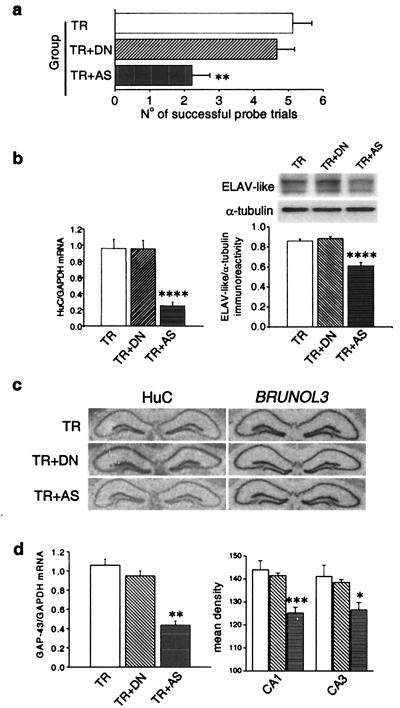
Figure 4.
Behavioral and biochemical effects of antisense-mediated knockdown of HuC gene expression in mouse brain. (a) Performance in the probe session of the radial maze task in sham controls (TR) and in mice daily infused during the training with fully sequence-degenerate (TR + DN) or anti-HuC antisense (TR + AS) oligonucleotides (n = 9 for TR animals and n = 8 for TR + DN and TR + AS animals). Data are expressed as means ± SEM (**, P < 0.01, post hoc analysis between DN-treated and AS-treated mice). (b) Effect of the anti-HuC antisense treatment on HuC gene expression. (Left) Real-time quantitative RT-PCR determination of HuC mRNA steady-state levels normalized to GAPDH levels. (Right) (Upper) Representative Western blot of the overall ELAV-like immunoreactivity in the three groups of mice compared with α-tubulin. (Lower) Means ± SEM, n = 6 each group for both mRNA and protein determinations. ****, P < 0.001, post hoc analysis between DN-treated and AS-treated mice. (c) Sequence specificity of the antisense-mediated HuC gene expression down-regulation. Representative in situ hybridizations showing hippocampal mRNA levels for the HuC and for the phylogenetically related BRUNOL3 genes in the AS ODN-treated and the two control mice groups. (d) Effect of the anti-HuC antisense treatment on GAP-43 gene expression. (Left) Real-time quantitative RT-PCR determination of GAP-43 mRNA levels normalized to GAPDH levels in the hippocampi of the three groups of mice (means ± SEM, n = 6 for each group; **, P < 0.01, post hoc comparison between DN-treated and AS-treated mice). (Right) Densitometric analysis of GAP-43 mRNA levels in the CA1 and CA3 hippocampal subfields from in situ hybridization performed on brain slices of the same mice (means ± SEM, data collected from five to seven mice from each group; *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.005).