Figure 2.
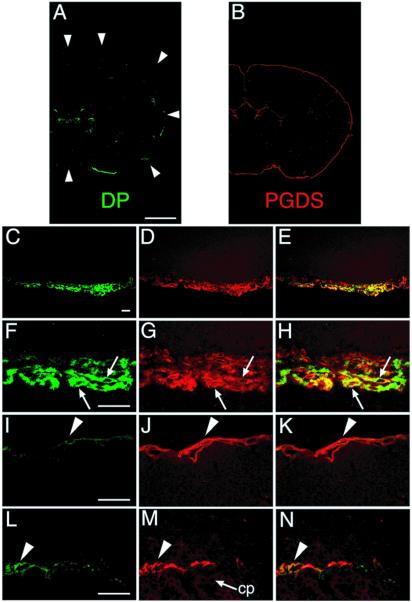
Double-immunofluorescence labeling of both DP and PGDS in WT mouse brain. Serial coronal sections were stained with two antibodies, one against DP (green; A, C, F, I, and L) and the other against PGDS (red; B, D, G, J, and M). Typical immunofluorescence-positive images (A–D, F, G, I, J, L, and M) and merged images (E, H, K, and N) are shown. (A) A coronal section 0.2 mm caudal to the bregma. The faint staining in the subcentral area is not associated with the choroid plexus. The circumference of the brain is outlined by the arrowheads. (B) A coronal section 0.5 mm caudal to the bregma. (C–E) A coronal section 0.1 mm caudal to the bregma. (F–H) A coronal section at the bregma. Arrows indicate the LM cells expressing both DP and PGDS. (I–K) A coronal section 3.5 mm caudal to the bregma. Arrowhead indicates the PGDS-expressing LM cells of the occipital cortex. (L–N) A coronal section 2.3 mm caudal to the bregma. The DP immunoreactivity was weakly detected in the neighboring LM cells at the ventricles (arrowhead) but not in the epithelial cells of the choroid plexus (cp). (Bar in A and B, 1 mm; bar in C–E, 30 μm; bar in F–N, 20 μm.)