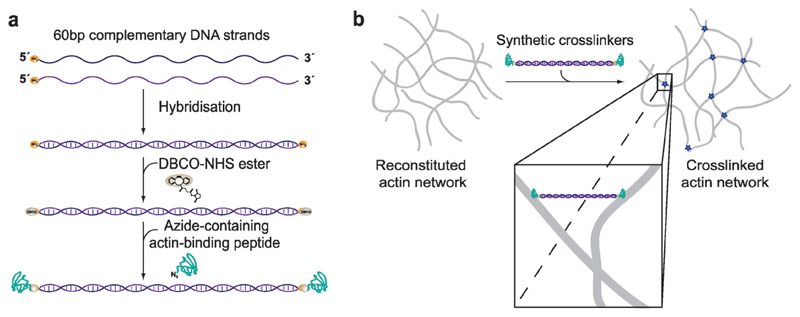
Figure 1. Constructing synthetic actin crosslinkers.
a) A copper-free click chemistry approach[19] was used to covalently attach two actin-binding peptides to double-stranded DNA. After hybridization of the complementary strands, dibenzocyclooctyne-NHS ester covalently reacted with primary amine groups on each end of the double-stranded DNA spacer. Subsequently, an azide-containing actin binding peptide formed a covalent bond with the previously attached DBCO group. b) Since the two binding domains were connected by double-stranded DNA, the construct can physically crosslink actin filaments within the system.