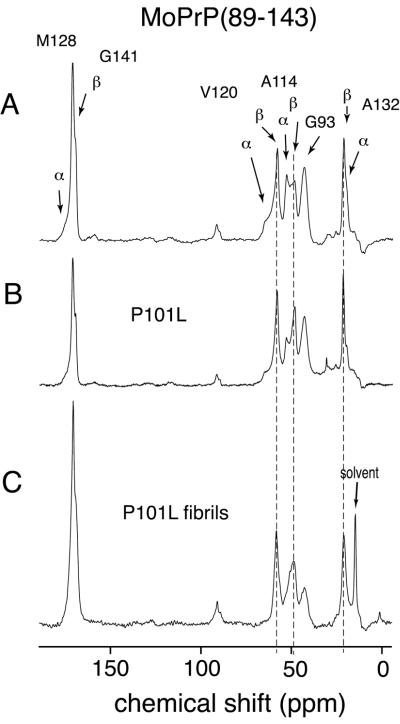
Figure 2.
One hundred twenty-six-megahertz solid-state 13C CPMAS spectra of wt mouse PrP(89–143) obtained at a spinning speed of 10 kHz. (A) wt MoPrP(89–143) spectrum, with the sample dried from water. Arrows indicate the resonances, which occur at characteristic shifts for helical and extended (sheet) conformations. The resonance from the carbonyls of G141 in a helical conformation and M128 in the extended conformation overlap, and so cannot be distinguished. (B) Spectrum of MoPrP(89–143, P101L) dried from water. (C) Spectrum of MoPrP(89–143, P101L) peptide after conversion to fibrillar form by precipitation from acetonitrile/water. The lines superimposed over the resonances for V120, A114, and A132 mark the β-sheet chemical shifts. The higher ratio of β-sheet to helical resonances in the unaggregated mutant MoPrP(89–143, P101L) indicates the preference for this mutant to adopt β-sheet structures. This preference for β-sheet structures was enhanced by exposure of the mutant peptide to acetonitrile/water (C) where the helical resonances have almost disappeared.