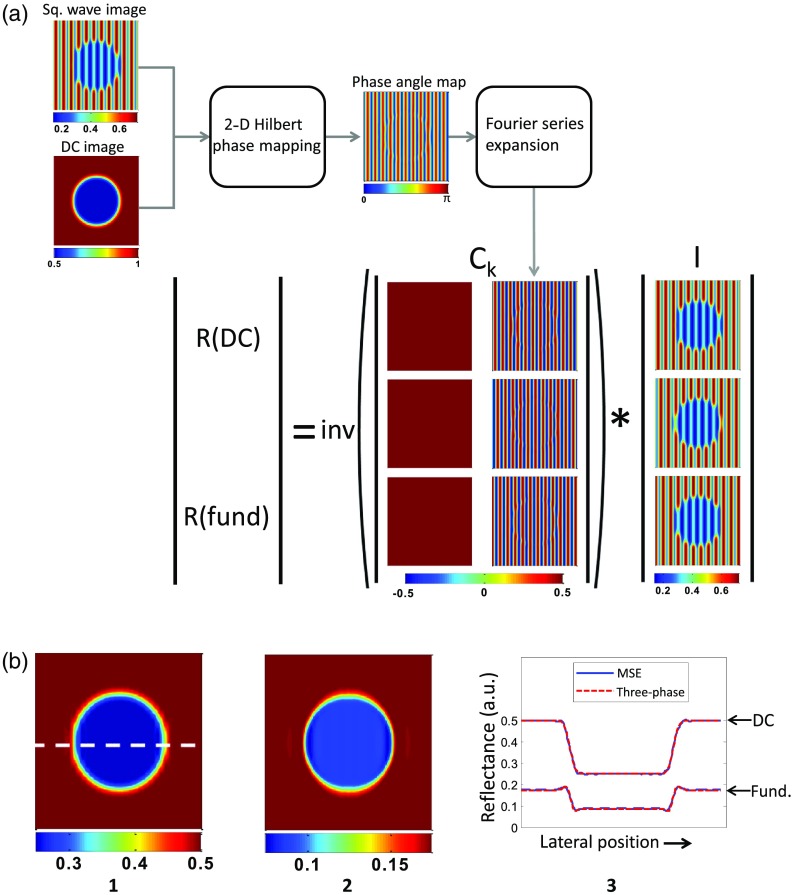
Fig. 2.
(a) Simulated workflow of multifrequency synthesis and extraction (MSE) algorithm on a turbid sample containing a circular absorbing lesion. First, a square wave () and a DC (planar) image are acquired. Here, the low-pass filtering properties of the sample damp the higher-ordered harmonics of the square wave, such that only the fundamental frequency component is preserved. These images are applied to a two-dimensional Hilbert transform method, from which the phase angle map of the square wave pattern is derived. Using the known Fourier series representation of a square wave [Eq. (3)], the frequency coefficient matrix () is generated. Finally, is inverted and multiplied by the raw data vector (). (b) Extracted spatial frequency intensities from simulation shown in (a), including (1) DC and (2) fundamental frequencies. (3) Cross-section of extracted reflectance comparing MSE to conventional, three-phase SFDI.