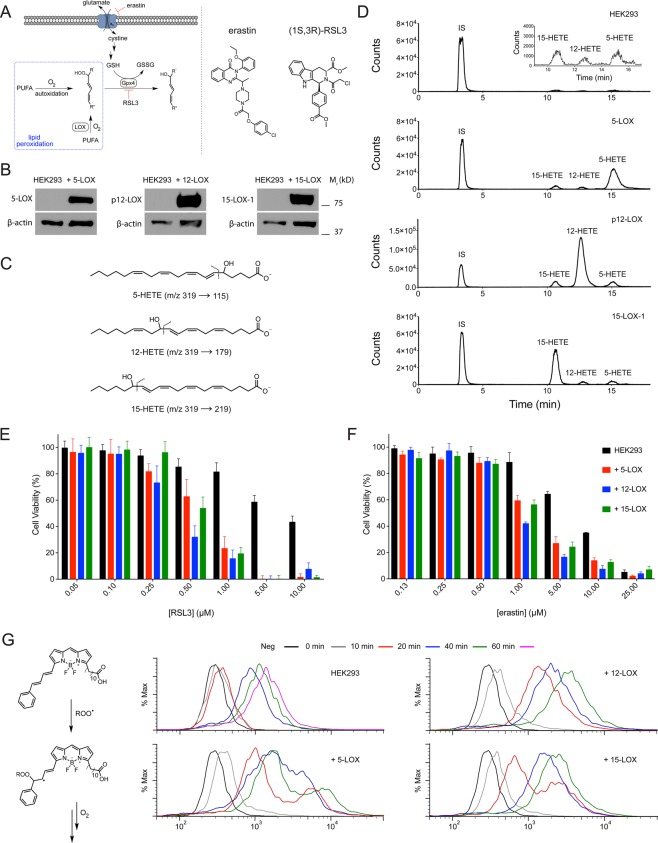
Figure 1.
(A) Formation of cellular lipid hydroperoxides (LOOH) occurs primarily by iron-accelerated free radical autoxidation and LOX-catalyzed oxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids. (B) Overexpression of 5-LOX, platelet 12-LOX, and 15-LOX-1 in HEK293 cells. (C) MS/MS transitions for the 5-, 12-, and 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs) produced by the overexpressed LOXs. HETEs were analyzed following reduction of the corresponding hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HPETEs) with TCEP. (D) LC/MS/MS chromatograms of organic extracts of cell lysates following incubation with 70 μM arachidonic acid for 10 min. (E, F) RSL3- and erastin-induced ferroptosis in each cell line following 4 and 24 h incubation, respectively. Data represent the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments (P < 0.0001 and P ≤ 0.001 for LD50 values of RSL3 and erastin as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). (G) Flow cytograms of C11-BODIPY-treated cells supplemented with 70 μM AA.